
When you're translating technical documents, you’re doing more than just changing words from one language to another. You’re ensuring absolute precision. A single wrong term in an engineering schematic, a user manual, or a patent filing can cause equipment to fail, create serious safety hazards, or spark major legal battles.
It’s a specialized field where deep subject-matter knowledge has to meet linguistic skill to keep every critical detail intact.
Why Flawless Technical Translation Is Mission-Critical

The stakes couldn't be higher. With marketing or creative content, you often have some wiggle room for interpretation. Technical translation is the complete opposite—it’s all about rigidity and unwavering accuracy.
Think of it this way: translating a poem is one thing, but translating the blueprint for a skyscraper is another. One small mistake in the blueprint could lead to a real-world disaster. The process demands a meticulous approach to make sure complex jargon, proprietary terms, and intricate instructions come across perfectly in the new language.
The Real-World Impact of Precision
Even a tiny inaccuracy can snowball into a massive problem. A poorly translated instruction in a medical device manual might put a patient’s life at risk. An error in a legal patent document could invalidate intellectual property rights, costing a company millions.
Here, precision isn’t just a nice-to-have; it's the absolute baseline.
The main hurdles you'll face are pretty consistent across projects:
- Complex Terminology: Every technical field is loaded with its own jargon, acronyms, and niche phrases that often have no direct one-to-one equivalent.
- Formatting Integrity: These documents are rarely just text. They contain crucial tables, diagrams, complex equations, and even code snippets that must be perfectly preserved.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many technical documents, from pharmaceutical inserts to manufacturing specs, must follow strict international standards and local laws that also need accurate translation.
The goal is simple: the translated document must function exactly like the original. Any ambiguity or error introduces risk, weakens the document's purpose, and can create massive liability.
Beyond Words on a Page
Getting this right often comes down to a deep understanding of language itself. It’s not just about understanding the source text, but being able to produce an equally accurate and functional text in the target language. It's similar to the distinction between comprehension and production in language that linguists talk about.
This is exactly why a professional, structured workflow is so important. It marries human expertise with powerful tools to manage terminology, keep everything consistent, and validate accuracy from start to finish. In this guide, I'll walk you through how to build a workflow that does just that.
Setting Your Documents Up for Translation Success

The secret to a smooth project happens long before a single word gets translated. It all starts with preparing your source files. This upfront work—think of it as a pre-flight checklist for your content—is what prevents costly errors and endless revisions down the road.
Honestly, it's about setting the stage. A clean, well-structured document is far easier for any translation system, whether AI or human, to process accurately. A messy one, full of inconsistent formatting and ambiguous terms, is just a recipe for confusion.
Mastering Your Source Files
Your very first job is to clean up the source document itself. Whether you're working with a DOCX, EPUB, or even a notoriously tricky PDF, consistency is your best friend. Inconsistent styling, where one heading is Arial 14 Bold and another is Times New Roman 14 Bold, can completely throw off translation software and create a jumbled mess.
The goal here is simple: simplify and standardize. It's also worth remembering that great translation starts with great writing, so taking a moment to understand how to write technical documentation effectively will pay dividends.
Here are a few practical steps I always take:
- Standardize Your Styles: Don't just manually format text. Use the built-in style features in your word processor, like "Heading 1," "Heading 2," and "Body." This creates a logical structure that translation tools recognize and replicate perfectly.
- Kill the Extra Formatting: Hunt down and eliminate unnecessary double spaces, manual line breaks, and random tabs. These tiny issues snowball into major formatting headaches in the translated version.
- Check for Consistency: Make sure all sections follow the same layout rules. This one step will make the final translated document look professional and polished.
For a deeper dive, you might want to explore our list of the best tools for translation-friendly formatting. Many of them can automate this cleanup process for you.
Building a Glossary and Style Guide
With the file tidied up, it's time to manage your language. Technical documents are packed with proprietary terms, acronyms, and specific phrases that absolutely must be translated the same way every time. This is what a glossary is for.
A glossary is simply a list of your key terms and their approved translations. It’s the single source of truth for your project. For instance, if your product is called the "Hyper-Spanner," the glossary ensures it isn't accidentally translated as "Mega-Wrench" in one chapter and "Super-Key" in another.
If you do one thing, do this: create a robust glossary. It is the single most effective action you can take to guarantee terminology consistency across thousands of pages. It removes all the guesswork for the translator and solidifies your brand’s voice.
Your style guide works hand-in-hand with the glossary. It defines the project's tone, voice, and formatting rules. Should the tone be formal or conversational? How should dates and measurements be formatted in Spanish versus Japanese? The style guide answers these questions, giving everyone on the project a clear roadmap.
Handling Embedded Text and Visuals
A classic hurdle in technical translation is text locked inside images, charts, and diagrams. Translation software usually can't "see" this text, which means critical information—like labels on a schematic or data points on a graph—gets left behind.
You have a few ways to tackle this challenge:
- Extract the Text: The best option is to recreate the graphic with editable text layers. If you can, provide the translator with the source files (like Adobe Illustrator or Photoshop files) so they can directly edit the text.
- Create a Text Table: If you can’t edit the image, make a simple two-column table. In one column, list the text exactly as it appears in the image. The translator will put the translated version in the other column. You'll then need to manually update the graphic.
- Use Captions: For simpler visuals, you can get away with adding detailed captions that explain what's in the image. This text is easily translated and gives the reader the context they need.
By dealing with these elements before translation begins, you ensure no data is lost in translation. This proactive approach is what separates a seamless project from one plagued by delays and inconsistencies. Trust me, the time you invest in preparation pays for itself many times over.
Choosing the Right Translation Workflow
Deciding how to translate a technical document isn't a simple coin toss between a human and a machine. It's really about picking the right tool for the job. Your choice ultimately boils down to a classic project management triangle: your budget, your deadline, and what the document is actually for.
An internal service manual that needs to be ready for the team in Asia by tomorrow? A pure AI translation can be a lifesaver, delivering a perfectly usable draft almost instantly. But for something like a patent application, where one wrong word could cost millions, the precision and legal accountability of a human expert is the only way to go.
The Rise of AI in Technical Translation
Machine translation has been around for a while, but what we're seeing now with AI is a different beast entirely. The market has exploded, jumping from $450 million in 2017 to a staggering $1.1 billion in 2022.
That 144% surge, as highlighted in data from Tomedes.com, isn't just hype. It’s driven by AI's newfound ability to tackle dense, specialized content like scientific papers and engineering specs with a level of accuracy that was unthinkable just a few years ago.
Modern AI isn't just for a rough translation of an email anymore. It's a serious professional tool. These platforms can churn through massive documents in minutes, offering a speed that no human can ever hope to match. For high-volume projects or internal-facing documents, this makes AI an incredibly powerful and cost-effective starting point.
When a Human Translator Is Irreplaceable
Even with all of AI's advancements, some jobs absolutely require a human touch. Certain documents demand a level of critical thinking, cultural nuance, and professional liability that an algorithm simply can't provide.
Here are a few scenarios where a human expert is non-negotiable:
- High-Stakes Legal Documents: When you're dealing with patents, contracts, or regulatory filings, any ambiguity can open the door to legal nightmares. A professional translator provides linguistic and legal scrutiny that can be defended in court.
- Creative or Persuasive Content: Technical doesn't always mean dry. If your document is a product brochure or a user guide with marketing copy, a human can capture the persuasive tone and adapt it for the target culture in a way AI struggles with.
- Safety-Critical Information: Think medical device instructions or manuals for operating heavy machinery. The risk of a misunderstanding is far too great. A human expert ensures every warning is perfectly clear and culturally appropriate.
In these cases, the higher cost of a human translator isn't an expense; it's an investment in mitigating risk.
The Hybrid Model: The New Gold Standard
For the vast majority of technical documents today, the most effective strategy is a hybrid model. This approach, often called Machine Translation Post-Editing (MTPE), gives you the best of both worlds. It perfectly balances speed, cost, and quality.
The process is straightforward but powerful:
- AI First Pass: The document gets an initial translation from a high-quality AI engine. This does the heavy lifting, translating thousands of words in just a few minutes.
- Human Refinement: A professional translator—who is also an expert in the subject matter—steps in to review and edit the AI's output. They fix errors, smooth out clunky phrasing, enforce consistent terminology, and add the necessary cultural nuance.
This hybrid workflow has become the industry standard for a reason. You get a human-quality translation at a fraction of the cost and time of a traditional, fully manual process. It’s the raw speed of AI guided by the critical eye of an expert.
This is the sweet spot for large projects like user manuals, extensive knowledge bases, and detailed technical specifications.
To help you decide, here’s a quick breakdown of how these workflows stack up against each other for technical content.
Translation Workflow Comparison
| Workflow | Speed | Cost | Best For | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AI Only | Instant | $ | Low-risk, internal documents; getting the gist | Internal R&D notes, initial draft for review |
| Human Only | Slow | $$$ | High-risk, legally binding, or creative content | Patent applications, medical device manuals, marketing brochures |
| Hybrid (MTPE) | Fast | $$ | Large-volume technical guides, manuals, and reports | A 500-page software user manual, engineering specifications |
Ultimately, the goal is to find the right balance for your project. By exploring the different types of document translator software, you can find platforms that integrate these powerful workflows and help you confidently and efficiently translate any technical document.
Tackling the Twin Dragons: Terminology and Formatting
Ask anyone who's managed a technical translation project, and they'll tell you where the real nightmares live. It’s not just about the words; it’s about consistency and presentation. An "actuator assembly" on page 5 can't magically become a "drive mechanism" on page 500. And that perfectly labeled schematic? It's useless if the translation blows up the layout.
Getting these two things right isn't about luck. It's about having a smart process and the right tools in your corner. Let's walk through how to tame these two common project-killers.
Your Secret Weapon for Consistency: Translation Memory
Imagine having a perfect, photographic memory for every single phrase you've ever translated. That's the core idea behind a Translation Memory (TM). It’s a living database that stores every approved translation segment—usually a sentence or a self-contained phrase.
When you kick off a new project, the TM software scans your document and instantly flags any segments it recognizes. If it finds a match, it pops in the pre-approved translation. For technical content, which is famously repetitive, this is a massive win. Think of all those standardized warnings, UI instructions, or component descriptions.
The impact is huge. It's no surprise that over 82.5% of professionals rely on TM technology. We're talking about slashing update costs by 20-30% and cutting delivery times in half. It’s not uncommon to see translator productivity jump by 30%. For things like software manuals or financial reports, a TM isn't just nice to have; it's essential. You can dig into more of these stats over at Redokun.com.
A Translation Memory isn't just an efficiency hack—it's your first line of defense against inconsistency. If you're regularly updating technical docs, a TM is non-negotiable for keeping your brand voice and technical accuracy locked down.
This decision tree gives you a good visual of how these tools fit into the bigger picture.
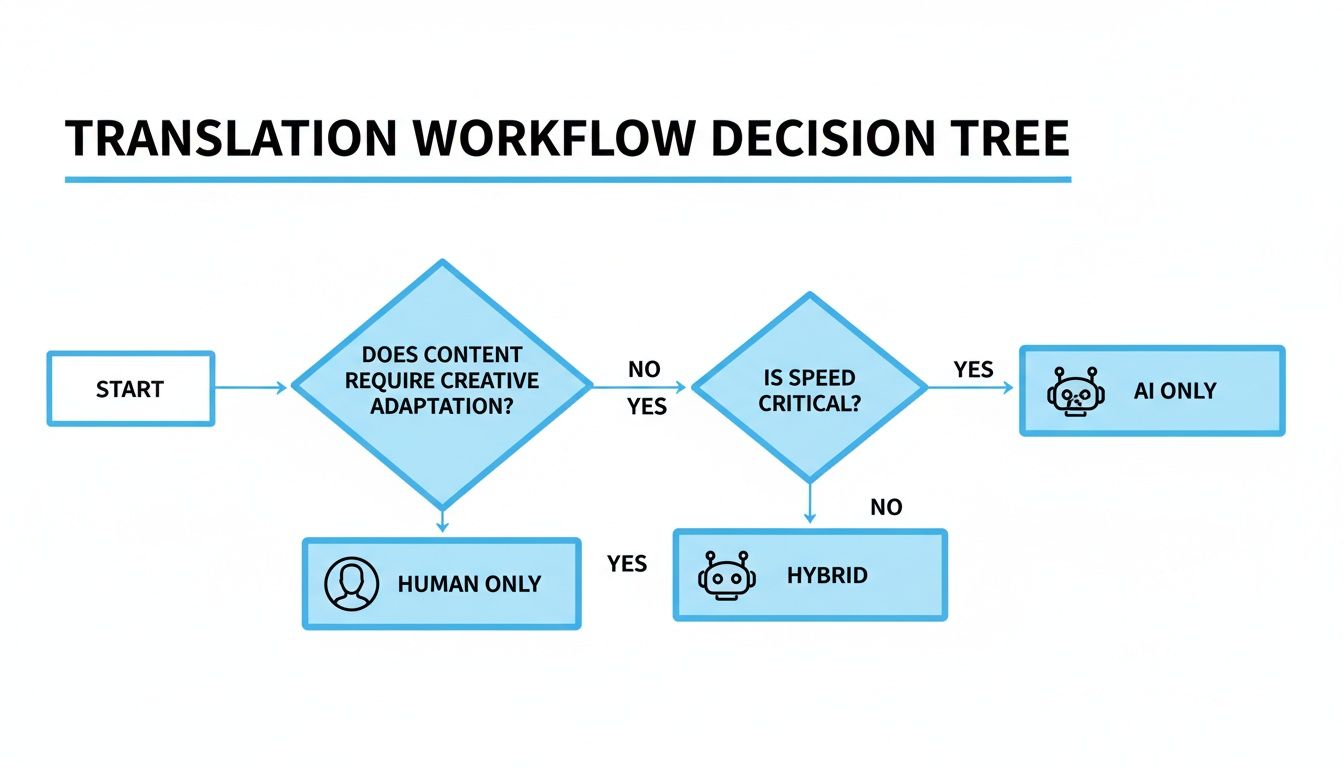
As you can see, figuring out whether to go with AI, human, or a hybrid workflow really comes down to your priorities for speed, cost, and quality.
Keeping Your Layouts Intact
The second headache is formatting. Technical documents are more than just words; they're structured, visual guides full of tables, equations, diagrams, and code snippets. One clumsy translation pass can turn a clean layout into a complete mess.
A classic culprit is text expansion and contraction. When you translate from a concise language like English into a more verbose one like German, the text can swell by up to 30%. Go the other way into a character-based language like Chinese, and it shrinks. This expansion can completely wreck your layouts, causing text to spill out of tables or throw off image alignments.
So, how do you stop your beautiful document from self-destructing?
- Use Tables for Structure: Forget about using tabs and spaces for alignment. Build your layouts with tables (you can always make the borders invisible). They're far more resilient to text flow changes.
- Embrace Whitespace: When designing the source document, be generous. That extra buffer you leave around images and inside table cells will be your best friend when the German translation needs more real estate.
- Isolate Text in Graphics: If you have text embedded in charts or diagrams, the only reliable method is to extract it, get it translated, and then have a designer re-integrate it into a localized version of the graphic. Don't just hope for the best.
- Deal with Tricky Files: Some formats are inherently difficult. Scanned PDFs, for example, are basically flat images of text. In these cases, you need a specialized workflow. It's crucial to learn how to translate a scanned PDF using tools with Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to make the text editable first.
A Quick Sanity Check for Formatting
Before you hand off any file, run through this mental checklist. It will save you a world of pain later.
- Is all the text actually text? Make sure nothing is trapped inside a flattened, non-editable image.
- Are styles consistent? Use formal styles like "Heading 1" or "Caption" instead of just manually bolding or changing font sizes. This gives translation tools the structural cues they need.
- Is there breathing room? Eyeball your layouts. Do they look cramped? If so, expanded text will break them.
- Are the tables clean? Avoid overly complex nested tables or randomly merged cells. Simple, clean tables are what translation software loves.
By pairing a solid Translation Memory system with a bit of foresight on formatting, you can sidestep the two biggest causes of frustration in technical translation. What was once a complex, unpredictable task becomes a much smoother, more reliable process.
Polishing the Final Product: Quality Assurance and Review
A translation isn’t really finished once the last word is translated. The final, and arguably most critical, phase is a thorough quality assurance (QA) process. This is where you hunt down and fix the errors before they ever see the light of day.
Skipping this step is like building a car and never taking it for a test drive. You're just crossing your fingers and hoping for the best, and when it comes to technical documents, hope is not a strategy. This final review ensures every single element, from the complex jargon down to the last comma, is precise, professional, and ready for your audience.
Editing vs. Proofreading: They’re Not the Same Thing
People often use "editing" and "proofreading" interchangeably, but in a professional workflow, they are two completely different—and equally vital—stages. Knowing the difference is crucial for a truly polished final document.
Editing is the deep-dive. The editor is focused on the substance and flow of the text. They’re asking:
- Does it sound natural? Is the language clunky, or does it read smoothly for a native speaker?
- Is the tone right? If the source text was formal and academic, the translation needs to reflect that same voice.
- Is the meaning crystal clear? The editor's job is to ensure no nuance was lost in translation and that the core message remains just as powerful.
Proofreading, on the other hand, is the final surface check. Think of the proofreader as a meticulous inspector looking for objective mistakes.
- Hard errors: This means typos, grammatical slips, and punctuation mistakes.
- Formatting glitches: Are there weird extra spaces? Did a heading style get applied incorrectly?
- Consistency check: The proofreader confirms that numbers, dates, and key terms from your glossary are used correctly and consistently from beginning to end.
A top-tier translation needs both. Editing makes it sound right; proofreading makes it look perfect. One without the other is a job half-done.
The In-Country Review: Your Ultimate Reality Check
One of the most powerful QA steps you can take is the in-country review. This means getting a subject matter expert (SME)—who is also a native speaker living in the target country—to put their eyes on the translation.
This person isn't just looking for typos. Their real value is in confirming two critical things:
- Technical Authenticity: Does the terminology match what professionals in that specific country actually use? An engineering term popular in Spain might be completely different from the one used in Mexico.
- Cultural Resonance: Are there any phrases, examples, or even images that might come across as confusing, awkward, or inappropriate to the local audience?
This step closes the gap between a translation that is linguistically correct and one that is truly effective and trustworthy for the people who will actually use it. It's your last line of defense against those subtle but critical mistakes.
Your Final QA Checklist
Before you sign off on any project, run through a final, methodical check. The global language services industry, valued at $64.7 billion in 2022, is built on these kinds of meticulous processes. This is why modern translation management software is so essential; it can cut the costs tied to human error by up to 90%. You can dig deeper into these translation industry trends to see how technology is shaping the field.
Use this list as a guide for your final pass:
- Glossary Check: Randomly spot-check 10-15 key terms to make sure they match what’s in your approved glossary.
- Numbers and Dates: Confirm all numbers, currencies, dates, and measurements have been properly localized (e.g., using a comma instead of a period for a decimal).
- Headers and Footers: Are all headers, footers, and page numbers correct and consistent? It's an easy thing to miss.
- TOC and Links: Click through the table of contents and a few internal hyperlinks. Do they take you to the right place?
- Visuals and Layout: Do a final visual sweep. Are all the graphics in place? Is the layout clean, with no text overflowing its box or getting cut off?
- File Naming: Ensure the final files are named according to your project specs and are delivered in the right format.
By running this structured QA process, you shift from hoping for an accurate translation to guaranteeing a polished, professional document you can release with total confidence.
Your Technical Translation Questions, Answered
If you're new to translating technical documents, you probably have a lot of questions about how it all works, especially when it comes to cost and turnaround times. Let's break down some of the most common questions I hear from clients.
How Much Should I Expect to Pay for Technical Translation?
This is the big one, and the honest answer is: it depends. The price tag is a moving target based on the languages involved, how dense the subject matter is, and the translation method you choose.
A fully human translation is the traditional route. You’re typically looking at $0.10 to $0.25 per word. So, for a 50,000-word user manual, you could be spending anywhere from $5,000 to $12,500. You're paying for a high level of human oversight and nuance.
On the other end of the spectrum, specialized AI translation platforms can process that same document for less than $10. It's an incredible value, especially for internal drafts or documents where the main goals are speed and cost-efficiency.
Many people land on a hybrid approach—AI translation followed by human post-editing. This gives you a professionally polished final product without the high cost of a fully manual job, making it a go-to for many large-scale technical projects.
What’s the Real Difference Between Translation and Localization?
People often use these terms interchangeably, but they are two very different things. Getting this right is crucial if you want your documents to actually connect with a global audience.
Translation is about the words. It’s the direct process of converting text from one language to another while staying true to the original meaning. It asks, "Can a reader in another language understand this?"
Localization is a much bigger-picture adaptation. It’s about making the entire document feel like it was created for the local market. For a technical manual, that means digging into the details:
- Units of Measurement: Swapping inches for centimeters or pounds for kilograms.
- Formatting: Adjusting date formats (DD/MM/YYYY vs. MM/DD/YYYY) or number separators (a comma or a period for the decimal point).
- Cultural Context: Making sure symbols, colors, and even images make sense and don't cause confusion or offense.
- Legal & Regulatory Standards: Ensuring the content complies with local industry standards and regulations.
Think of it this way: translation ensures your document is understood. Localization ensures it feels native and works correctly in a new market.
Can I Just Use a Free Online Translator for This?
For a quick, informal translation of an email? Sure. But for a professional technical document where every detail matters, free tools like Google Translate are simply not up to the task.
These general-purpose tools have some serious flaws. They can't handle glossaries, so your key terminology will be all over the place. They also tend to completely mangle complex formatting in tables, diagrams, and equations, leaving you with a mess.
The biggest issue, though, is security. When you upload a file to a free online service, you have no real control over where that data goes. For any document containing proprietary or confidential information, using a secure, professional platform isn't just a suggestion—it's a necessity.
How Long Will It Take to Get My Document Translated?
The timeline really comes down to which workflow you choose. It can be a matter of minutes or a project that spans several weeks.
A professional human translator generally works through about 2,000 to 2,500 words per day. For our 50,000-word manual example, that means you're looking at a four to five-week timeline, and that's before you factor in project management and quality checks.
AI-powered platforms work on a totally different clock. An AI can translate that same 50,000-word document in just a few minutes. The speed is almost hard to believe, and it’s a game-changer for projects with tight deadlines.
The hybrid model, as you'd expect, falls somewhere in the middle. The initial AI pass is nearly instant, and the overall timeline then depends on how much post-editing is needed. Your project's deadline will be a huge factor in deciding which path makes the most sense.
Ready to translate your technical documents with the speed of AI and the quality of an expert? BookTranslator.ai offers a powerful, intuitive platform that preserves your formatting and ensures consistency. Get started with your first translation today.