
Translating a document from Arabic to English is so much more than a word-for-word swap. You're not just converting a language; you're navigating entirely different scripts, page layouts, and deep-seated cultural contexts. It’s a process that bridges two distinct linguistic worlds, and frankly, winging it just won't cut it. This guide is your practical roadmap, whether you're an author, a researcher, or a business professional trying to get your message across accurately.

Your Guide to Arabic to English Document Translation
Let’s be clear: when you decide to translate a document from Arabic to English, you’re taking on one of the more challenging language pairs out there. The obstacles aren't just about vocabulary; they're baked into the very structure of how information is presented.
For starters, Arabic is a right-to-left (RTL) language, while English is left-to-right (LTR). This fundamental difference throws a wrench into everything—page layouts, numbering, the orientation of tables, even simple bullet points. If you just dump the text into a standard converter without the right tools, you'll end up with a jumbled, unreadable mess. I've seen it happen countless times.
Then you have the rich cultural layer. The Arabic language is brimming with idioms, metaphors, and religious expressions that often have no direct parallel in English. A literal, machine-like translation can sound clunky and unnatural, or worse, completely misrepresent the original author’s intent.
Overcoming the Core Challenges
The secret to a smooth translation is anticipating these hurdles from the get-go. A successful project always comes down to paying close attention to a few critical areas:
- Script and Layout: You have to manage the switch from RTL to LTR without completely scrambling the document's formatting.
- Cultural Nuance: It’s about capturing the meaning behind idioms and culturally specific phrases, not just their literal definitions.
- Dialectal Variation: You need to recognize that Arabic isn't monolithic. A common phrase in Egyptian Arabic might mean something different—or be completely foreign—in Gulf Arabic.
- Technical Consistency: For academic, legal, or technical documents, ensuring that key terms are translated the same way every single time is non-negotiable.
A strong Arabic-to-English translation shows care, builds trust, and helps your message resonate with a global audience. It's about making your content feel natural and understood, without any hint of confusion or awkward phrasing.
This guide is built to give you actionable strategies for each of these points. We’ll skip the generic advice and walk through a real-world workflow, whether you're using an AI-powered service like BookTranslator.ai or collaborating with a human editor. The goal is to produce a final document that is not only accurate but also professional and culturally attuned.
Get Your Arabic Document Ready for a Flawless Translation
The final quality of your English translation is pretty much decided before a single word is even translated. Honestly, the success of your project to translate a document from Arabic to English comes down to the prep work you do upfront. Think of it as laying a solid foundation for a house—if you skimp on this part, you're just asking for frustrating errors and expensive fixes later.
The main goal here is to start with a source file that's as clean and well-organized as possible. A well-formatted DOCX or EPUB file is your best friend. Why? Because these formats hold onto all the important structural stuff like chapter breaks, headings, and paragraph styles, which makes it much easier for translation software to understand the layout. A messy file with weird formatting, on the other hand, is a guaranteed headache.
Start with a High-Quality Source File
I've seen so many translation projects go wrong because of low-quality scans or badly converted PDFs. If the text is blurry or has weird digital smudges, the Optical Character Recognition (OCR) software just can't pull the Arabic script out accurately. You end up with garbled source text, which, no surprise, gives you a completely nonsensical translation.
If you're working with a scanned document, a critical first step is learning how to translate scanned PDF files. Taking that extra time to turn a scan into clean, editable text is probably the single most important thing you can do for accuracy.
Another common roadblock? Text that's part of an image. Translation tools can't read text locked inside a JPEG or PNG. You’ll have to pull that text out yourself and either pop it into the main document or provide it in a separate file for the translator.
Deal with Complex Formatting and Fonts
Arabic documents can be tricky. They often have elements that need some special handling before you even think about translation. For example, some documents use custom or non-standard Arabic fonts that translation systems might not recognize. A good rule of thumb is to switch the text to a universally supported font like Arial or Times New Roman. This simple change can prevent a lot of character-reading errors.
Complex tables are another beast entirely. A table with merged cells, fancy layouts, or text running in different directions can get completely mangled when it's flipped from a right-to-left to a left-to-right layout.
Pro Tip: Before you start translating, take a look at your tables. If they're complicated, simplify them. Unmerge cells and, if you can, break one massive table into a few smaller, simpler ones. It feels like extra work, but trust me, it can save you hours of painful reformatting on the other end.
Create a Glossary for Important Terms
Finally, and this is a big one for technical, academic, or even literary texts: create a glossary. Consistency is everything. You don't want a key term like "النظرية النسبية" showing up as "Relativity Theory" in one chapter and "The Relativistic Principle" in the next. It just looks unprofessional.
Put together a simple list of your most important terms and decide on their official English translations. This list should include:
- Technical jargon from your specific field.
- Proper nouns like the names of people, places, or companies.
- Key phrases or concepts that repeat throughout the document.
This glossary becomes your rulebook, making sure all the critical vocabulary stays consistent from start to finish. Putting in this effort now will make the entire translation workflow smoother, faster, and far more accurate.
Choosing Your Translation Method: AI vs. Human Expertise
When you need to translate a document from Arabic to English, you've hit a critical fork in the road. Do you go with a fully automated AI solution, or do you bring in a human expert to polish the final product? The right answer really hinges on what you’re trying to accomplish.
An instant AI translation can be a lifesaver. Picture this: you're a student drowning in Arabic research papers for your dissertation. Your goal isn't literary perfection; it's to absorb the core arguments and data as quickly as possible. In this case, an AI-first approach gives you speed and affordability, letting you get to the heart of the material without delay.
Or maybe you’re just a curious reader who wants to dive into a foreign novel for fun. You don't need a flawless, publication-ready manuscript—you just want the story. Here, a raw AI translation delivers the plot and dialogue in seconds, opening up a world of literature that would otherwise be out of reach.
When Human Expertise Becomes Essential
But then there are times when nuance is everything. If you're an author preparing your Arabic novel for the global market, your unique voice, cultural references, and literary flair are what make the book yours. An AI might get the plot right, but it takes a human post-editor to make sure the artistry survives the journey into English.
This hybrid model—letting AI do the heavy lifting and a human add the finishing touches—really does offer the best of both worlds. The initial translation is fast and cost-effective, but the human review is where the magic happens. A good editor will smooth out awkward phrasing, fix idioms that don't quite land, and ensure the tone feels completely natural to an English-speaking reader. This is the go-to method for professional publications, business contracts, or any document where subtle meaning can make or break your message.
This decision tree can help you visualize which path makes the most sense based on your starting file type.
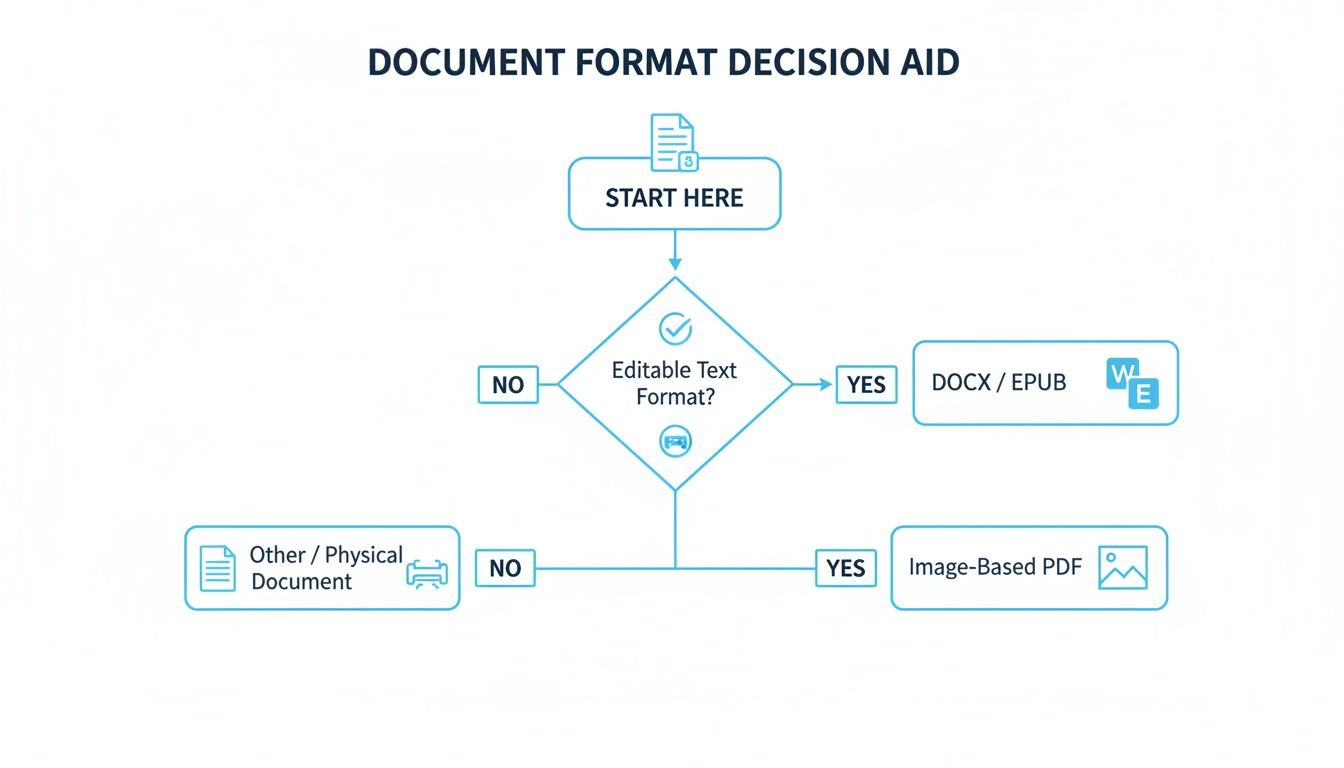
As the flowchart shows, starting with a clean digital file like a DOCX or EPUB makes the process much simpler. Scanned documents or PDFs, on the other hand, often need a bit more prep work to get the best results.
AI vs. Human-Edited Translation: Which Is Right for You?
So, how do you decide? This table breaks down the key differences to help you match the method to your project's specific needs.
| Feature | AI Translation (e.g., BookTranslator.ai Basic) | AI + Human Post-Editing (e.g., BookTranslator.ai Pro) | Best For |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speed | Near-instant. Get results in minutes. | Slower. Requires time for human review (days). | AI: When you need information immediately. |
| Cost | Highly affordable. The lowest-cost option. | Higher investment. Priced per word for expert time. | Human: When quality and nuance justify the cost. |
| Accuracy | Good for gist. Captures the core meaning well. | Excellent. Corrects errors and fine-tunes nuance. | Human: For professional, public-facing content. |
| Nuance & Style | Literal. Often misses cultural idioms and tone. | Culturally adapted. Preserves authorial voice. | Human: For creative works like literature and marketing. |
| Consistency | Very high. Uses consistent terminology throughout. | High. The editor ensures consistency and flow. | Both: AI sets a baseline, human refines it. |
| Use Cases | Research, personal reading, internal documents. | Book publishing, legal contracts, marketing materials. | AI: Understanding. Human: Publishing. |
Ultimately, choosing between pure AI and a human-edited translation isn't about which one is "better" in a vacuum—it’s about which one is the right tool for your job. For quick information gathering, AI is a powerful ally. For work that demands artistic integrity or cultural precision, that human touch is what makes all the difference.
The need for high-quality translation is exploding. The global language services market is on track to hit $147.48 billion by 2034, a massive leap from $56.18 billion in 2021. This incredible growth highlights just how much everyone, from authors to academics, relies on good translation. The technology driving this, especially in fields like AI copywriting, keeps getting better at producing human-like text. If you're curious about the engine under the hood, you might find our guide on what is neural machine translation an interesting read.
Navigating Right-to-Left Layout Challenges
When you translate a document from Arabic to English, the most jarring shift isn't just the language—it's the layout. Everything flips. Arabic is a right-to-left (RTL) language, and English is left-to-right (LTR). This isn't a simple text-align tweak; it's a fundamental restructuring of the entire page that can completely derail your document's professional look if you get it wrong.
Think about it: page numbers, bullet points, table columns, even the flow of chapters—they all need to be mirrored. If this isn't handled correctly, you end up with formatting disasters that scream "bad translation" from a mile away.
Common RTL to LTR Formatting Disasters
Have you ever opened a translated document and the page numbers are stuck on the left, where they'd be in an Arabic book? Or a numbered list where the numbers trail the text (e.g., "Here is my point .1")? It's confusing and instantly chips away at the content's credibility.
These are the kinds of headaches that pop up constantly. Here are a few specific gremlins I see all the time:
- Mirrored Tables: Data gets scrambled because columns that should be on the left are now on the right.
- Backward Numbering: Chapter and page numbers look completely out of order in English because they're still following an RTL sequence.
- Misaligned Graphics: Images with captions get flipped, so the caption ends up on the wrong side of the picture.
- Broken Punctuation: This is a classic. Full stops and commas appear at the beginning of a sentence instead of the end, which is a dead giveaway of a botched RTL-to-LTR conversion.
The goal is simple: the final English document should look like it was written in English. Any leftover RTL quirks are a red flag to the reader that the translation might have been a rush job.
Automating the Structural Shift
Imagine trying to fix every single one of these layout issues by hand, especially in a 200-page book. It’s a tedious, mind-numbing process that’s incredibly prone to error. You’d spend days just on formatting. This is precisely where modern translation tools become indispensable.
Platforms like BookTranslator.ai were built to solve this exact problem. They don't just swap words; they intelligently remap the document's entire architecture from RTL to LTR. This automated process handles the reorientation of all those tricky elements, saving you hours—or even days—of manual work. This is especially crucial for complex layouts, like scanned academic papers. For more on that, check out our guide on how to translate a scanned PDF.
The image below gives a great visual of how software has to wrestle with these opposing layouts to get things right.

This shows that text direction is a deep technical challenge, impacting everything from a single sentence to an entire user interface. Nailing this switch is non-negotiable if you want to produce a polished, professional English document from an Arabic original.
How to Ensure Accuracy and Cultural Nuance
Let's be honest: a direct, word-for-word translation can feel cold and lifeless. This is especially true when you translate a document from Arabic to English. The Arabic language is incredibly rich, packed with layers of cultural and historical meaning. A literal translation might get the words right, but it often completely misses the soul of the message, leaving you with something technically correct but emotionally empty.
This final quality check is what separates a decent translation from an exceptional one.

The real trick is learning to spot and fix the subtle things that AI often overlooks. Idioms, metaphors, and specific cultural references need a human eye to find an equivalent that actually connects with an English-speaking audience—not just a literal one that leaves them scratching their heads.
Practical Review Techniques for Better Flow
You don't have to be a professional editor to run a solid quality check. A few simple tricks can help you find awkward phrasing and unnatural rhythms that are easy to miss when you're just reading silently.
- Read It Aloud: This is the single best piece of advice I can give. When you read your translated text out loud, you force yourself to slow down. Your ears will catch clumsy sentences and robotic phrasing that your eyes just skim over.
- Get a Fresh Perspective: Find a native English speaker—even if they don't know a word of Arabic—and ask them to read a chapter. Their job isn't to check accuracy; it's to check for flow. If something sounds confusing or stilted to them, it's a clear signal that the translation needs work.
- Check for Consistency: Make sure key terms and names are spelled the same way throughout the document. A character named "خالد" shouldn't be "Khalid" in one chapter and "Khaled" in another. Small details like this make a huge difference.
Getting this right is more important than ever. The MENA region boasts a $2.5 trillion GDP, and as the GCC Translation Service Market on GlobeNewswire reports, the demand for quality translation is skyrocketing. With 88% of Arab consumers preferring content in their native language, the reverse is also true for global audiences. High-quality translation isn't just a nice-to-have; it's a must for anyone in finance, e-commerce, or publishing.
Preserving the Original Author's Tone
Beyond just fixing words, the real goal is to capture the author's original voice. Was the source text formal and academic? Poetic and literary? Or was it casual and conversational? The final English version needs to reflect that same tone to feel authentic.
A successful translation doesn't just convey information; it conveys feeling. It should read as if it were originally written in English, carrying the same style, rhythm, and intent as the Arabic source.
This is particularly crucial for authors trying to reach a new audience or for researchers whose findings depend on precise language. Capturing these subtleties is what turns a simple word conversion into a true translation. If you want to explore this further, our article explaining cultural nuances in AI book translation is a great place to start.
Your Top Arabic to English Translation Questions, Answered
If you're looking to translate a document from Arabic to English, you probably have a few practical questions on your mind. I hear the same ones all the time. Let's walk through the most common concerns, from budgeting to timelines, so you know exactly what to expect.
What’s the Real Cost to Translate from Arabic to English?
The price tag for translation can swing wildly, and it really comes down to the route you take. The old-school way involves hiring a human translator, who will typically charge you by the word. You can expect to pay anywhere from $0.10 to $0.25 per word, which sounds small until you do the math for a big report or a full book. That can easily run into thousands of dollars.
But today, AI-powered services have completely flipped the script. Tools like BookTranslator.ai work on a different model, often charging a small flat fee for a massive word count—think a few bucks for 100,000 words. This makes translation accessible for projects that would have been financially out of reach just a few years ago. Your final cost will usually depend on whether a standard AI translation is good enough or if you need the higher accuracy of a premium AI model for more delicate work.
Can I Actually Get a Good Translation from an Arabic PDF?
Yes, you can, but this is where most people get tripped up. Translating PDFs is a classic headache, especially if they're scanned documents. The text is often trapped inside an image, so if you just run it through a basic text translator, you'll get a mess of jumbled words and broken formatting.
The trick is to use a tool built specifically for document translation. These platforms are designed to see past the complex structure of a PDF and extract the text properly, preserving the layout in a way that generic apps just can't handle.
For the cleanest possible result, I always recommend converting the PDF to a DOCX file first if you can. It gives the translation engine a much simpler file to work with. Platforms designed for books are far more robust at managing tricky PDF layouts than your average online translator.
How Long Will It Take to Translate a 100-Page Document?
This is where you'll see the biggest difference between AI and traditional methods. Speed is, without a doubt, the most powerful advantage of using AI.
- AI Translation: A tool like BookTranslator.ai can churn through a 100-page document (which is about 25,000 words) in just a couple of minutes. Seriously.
- Human Translation: A skilled human translator can handle around 2,000 words a day. That same 100-page document would likely take them between 10 and 12 business days to finish.
If you need something done quickly—for market research, an internal review, or just to read a book for pleasure—AI is the obvious choice. Even for commercial projects, starting with an AI draft can slash your timeline, letting your human editor jump straight into polishing the text instead of translating from zero.
Will an AI Translation Keep the Original Arabic Tone and Style?
This is the million-dollar question, especially for authors and creatives. Modern AI is incredibly good at maintaining a consistent tone and nailing factual information. For technical manuals, academic papers, or business reports where precision is key, it does a fantastic job.
Where it can still struggle is with the deep, artistic stuff—the subtle literary voice, cultural inside jokes, and the unique rhythm of an author's prose. A standard AI translation might lose some of that magic. For novels, poetry, or marketing material where every word counts, I'd strongly suggest using a premium AI model or having a human post-editor review the output. That final human touch ensures the soul of the original work truly comes through in English.
Ready to share your Arabic documents with the world? With BookTranslator.ai, you can get a high-quality translation in minutes while keeping your original formatting intact. Translate your book now with BookTranslator.ai.