
Translating a document from Arabic to English can feel like a real puzzle. It's so much more than just swapping words. You're wrestling with right-to-left text, specialized fonts, and cultural subtleties that a simple machine translation will almost certainly miss. Think of this guide as your detailed roadmap, showing you how to blend the speed of AI with the irreplaceable insight of a human expert to get translations that are both accurate and professionally formatted.
A Practical Workflow for Arabic to English Document Translation

Turning an Arabic document into fluent, natural-sounding English takes more than just being bilingual—it requires a solid strategy. The path is full of potential tripwires, from technical formatting glitches to the kind of deep cultural nuances that can completely change a message. Whether you're working with legal contracts, academic research, or a full-length eBook, getting this right is non-negotiable.
A botched translation can create serious problems. Think of broken page layouts, embarrassing misunderstandings, or just a general loss of professional credibility. For example, a marketing slogan that's clever in English might come across as awkward or even offensive in Arabic if it’s translated word-for-word, ignoring local expressions.
And then there's the layout. The structural jump from a right-to-left (RTL) script to a left-to-right (LTR) format can completely shatter the visual appeal of a carefully designed document if you don't manage it properly.
What This Guide Covers
This guide lays out a practical framework for navigating these challenges. We’re going to go far beyond basic word replacement and dive into a complete workflow built for professional-quality results. Here’s what you'll learn:
- File Preparation: How to properly prepare your source files, dealing with common headaches like text direction and font compatibility to stop errors before they even happen.
- Choosing Your Method: Deciding when to use fast AI tools, when to rely on a skilled human translator, or how to combine them for the best of both worlds.
- Preserving Formatting: Techniques to ensure your final English document mirrors the professional layout and design of the original Arabic version.
- Quality Assurance: The crucial steps of post-editing and cultural validation that catch the subtle mistakes automated tools inevitably miss.
The real goal isn't just to translate the words on the page. It's to transfer the meaning, the intent, and the professionalism from one language to another. A great Arabic to English translation should read as if it were originally crafted for an English-speaking audience.
By following the steps outlined here, you can sidestep common frustrations and produce translations that are accurate, culturally sensitive, and visually polished. Whether you’re a business owner reaching new markets or an author looking to connect with a global audience, this process is key.
For those working on larger projects, specialized platforms like BookTranslator.ai can be incredibly helpful. They are designed to automate many of these tricky technical steps, especially for long-form content like books, by handling layout preservation and maintaining stylistic consistency across hundreds of pages. This guide will give you the foundational knowledge to tackle any project with confidence.
Getting Your Arabic Documents Ready for Translation
A top-notch translation from Arabic to English starts long before the first word is ever changed. Getting your source file in order is, without a doubt, the most important thing you can do to sidestep common headaches like scrambled text, broken layouts, and weird-looking characters. If you skip this prep work, you’re pretty much signing up for a longer, more expensive, and more frustrating project down the road.
The biggest hurdle comes from how the languages are written. Arabic is a right-to-left (RTL) script, while English is left-to-right (LTR). This isn't just about pushing text to one side of the page; it impacts everything—tables, numbered lists, even where images sit. A document that isn't set up to handle this switch can completely fall apart when you translate it.
Navigating Right-to-Left Formatting and Fonts
First things first, let's tackle the text direction. If you have an editable file, like a Microsoft Word document, you need to make sure the original Arabic is properly set to RTL. This simple setting is a signal to translation software, helping it understand the flow of the original and preserve the layout when it creates the English version.
Another classic mistake is using incompatible fonts. Arabic has beautiful, complex characters, and not all fonts are built to handle them. If your document uses an obscure or custom font, it might show up as a bunch of squares or gibberish on the translator's computer.
The easiest fix? Stick with well-known, Unicode-compliant fonts.
- For professional or official documents: Fonts like Arial, Times New Roman, or Calibri are your best friends. They have excellent Arabic character support and are available on virtually every computer.
- For branded or creative work: If you absolutely must use a specific font for branding, either embed it directly into the file (which you can do with PDFs) or send the font file along with the document. This keeps your design consistent.
A clean, well-formatted source document is the bedrock of a great translation. Spending just thirty minutes to sort out fonts and tidy up the file can save you hours of fixing layout disasters later on.
Before you send any file off for translation, a quick check can make all the difference. I've put together a simple table to run through.
Arabic Document Pre-Translation Checklist
This checklist covers the essential preparation steps that I always recommend to clients. It's a simple way to ensure the translation process is as smooth and accurate as possible from the very beginning.
| Checklist Item | Why It Matters | Actionable Tip |
|---|---|---|
| Confirm Text Direction | Prevents layout collapse when switching from RTL (Arabic) to LTR (English). | In your editor (e.g., Word), select all Arabic text and ensure the "Right-to-Left Text Direction" button is active. |
| Check Font Compatibility | Guarantees that Arabic characters will display correctly for the translator. | Convert text to a universal font like Arial or Times New Roman. If you can't, embed the font in the PDF or provide the font file. |
| Remove Unnecessary Formatting | Extra spaces, manual line breaks, and complex text boxes can cause major formatting errors in translation tools. | Use your editor's "Show/Hide" feature (the ¶ symbol) to find and remove double spaces, manual breaks, and other invisible formatting. |
| Verify OCR Accuracy (for scans) | OCR mistakes can alter critical data like names, dates, and numbers. | After running OCR, proofread the output against the original scanned image, paying close attention to numbers and proper nouns. |
| Provide Context/Glossary | Helps the translator understand industry-specific terms, acronyms, or brand voice. | Include a separate document with definitions for key terms, company-specific jargon, or notes on the desired tone. |
Following this checklist helps eliminate the most common sources of error and delay, setting your project up for success.
Turning Scanned Documents into Usable Text
What about documents that aren't digital to begin with? Think legal contracts, birth certificates, or old academic records that you only have as a scanned PDF or a JPG. You can't translate a picture of text. This is where Optical Character Recognition (OCR) comes in.
OCR technology scans the image, recognizes the Arabic letters, and turns them into editable text you can actually work with. But a word of caution: not all OCR tools are created equal, especially for a complex script like Arabic. The quality of the output can be a coin toss.
When you're starting with a scan, your first job is to process it with a high-quality OCR tool that is specifically trained for Arabic. You need software that can handle:
- Connected, cursive script: Arabic letters change their shape based on where they are in a word, a nuance that trips up basic OCR tools.
- Diacritics (Tashkeel): Those little marks above and below letters that indicate vowels are often essential for meaning, but many tools ignore them or get them wrong.
- Poor scan quality: A good OCR tool uses smarter algorithms to make sense of faded, blurry, or low-resolution text from older documents.
Once the OCR is done, you're not out of the woods yet. You have to manually review the text file it produced. Put it side-by-side with the original scan and hunt for errors. This is non-negotiable. One tiny OCR mistake—getting a number wrong in a contract or misspelling a name on a certificate—can cause massive problems. For really complex files, it's worth taking a deeper dive into advanced techniques for translating a scanned PDF to get the best possible results.
This careful prep work is what turns an unusable image into a clean, editable document, paving the way for a precise and reliable document translation from Arabic to English.
Choosing Your Translation Workflow
Once your files are prepped and ready, you hit a critical fork in the road. How will the actual translation get done? Are you going to rely on the raw speed of artificial intelligence, the careful nuance of a professional human translator, or a modern blend of both? This decision is the single biggest factor affecting the quality, cost, and timeline of your document translation from arabic to english.
There's no one-size-fits-all answer here. The best path for a simple internal manual is worlds away from what you’d need for a high-stakes legal contract or a beautifully written novel. It all comes down to your specific project and what you need to achieve.
This flowchart gives you a quick visual of how to think about the initial steps, which directly feed into the workflow you'll choose.
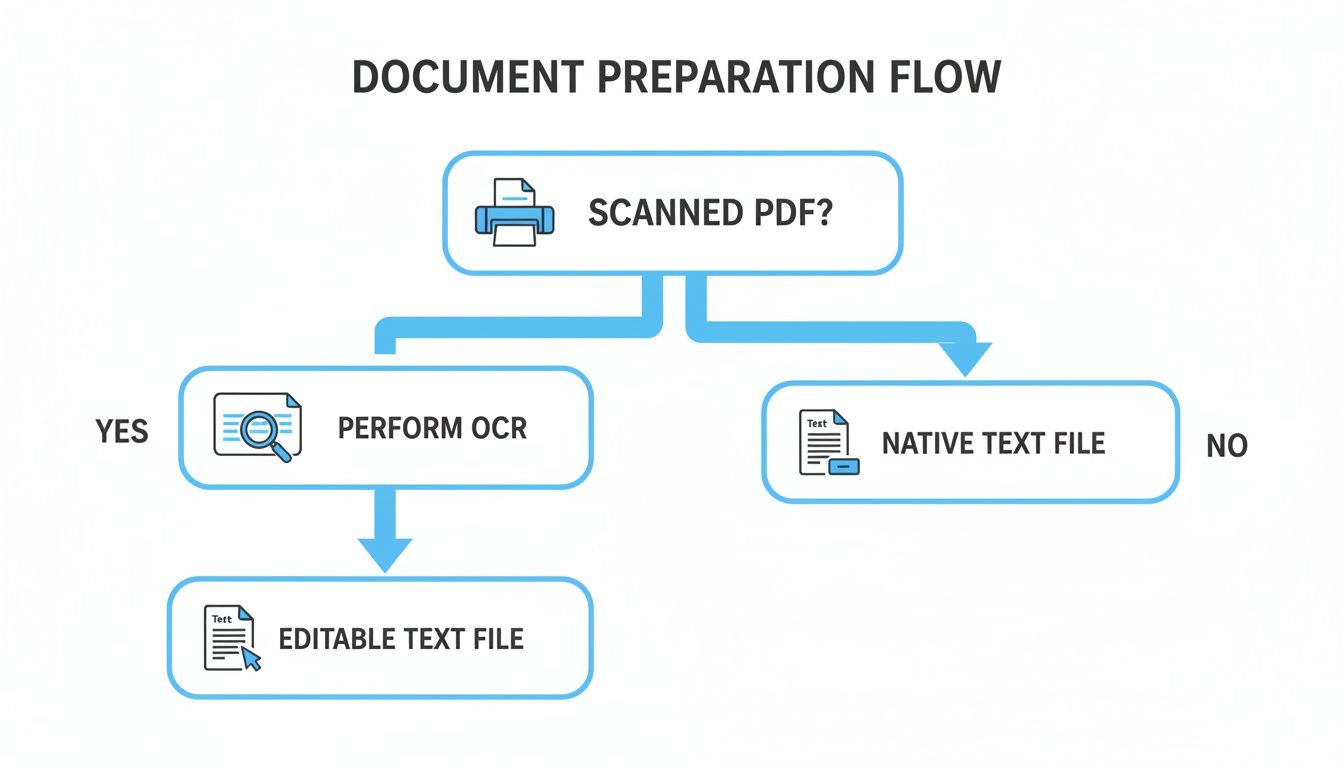
As you can see, the state of your document—whether it's a scanned image or an editable file—is the first decision point, often determining if you need to start with OCR.
The AI-First Approach: For Speed and Scale
AI-powered translation engines have become astonishingly good, churning out results almost instantly and at a tiny fraction of what human translation costs. If you're dealing with a massive volume of text and your main goal is just to get the gist of the content, an AI-first approach is often the most sensible choice.
Imagine a research team sifting through dozens of academic papers in Arabic. Using an AI tool, they can get a rough translation in minutes, letting them quickly pinpoint which papers are worth the investment of a full, professional human translation. The time and money saved are enormous.
But AI isn't a magic bullet, especially with a language as rich and complex as Arabic.
- It misses the nuance. AI translators are notorious for fumbling idioms, cultural references, and subtle shifts in tone that a human expert would catch in a heartbeat.
- Accuracy can be a gamble. While it's pretty reliable for simple, direct text, AI can make critical mistakes with complex sentences or ambiguous words.
- Formatting gets messy. Even the best tools can mangle a document's layout, particularly when dealing with the right-to-left to left-to-right shift.
The Human-Only Approach: For Precision and Polish
For any document where every single word matters, a professional human translator is non-negotiable. We're talking about legal contracts, certified immigration documents, high-impact marketing campaigns, and literary works. A human translator does more than just swap words; they adapt the core meaning, making sure the final English text is culturally spot-on, grammatically flawless, and carries the exact intent of the original Arabic.
Think about translating a marketing brochure. It's not about literal accuracy. A translator needs to understand the cultural mindset of the English-speaking audience to craft a message that actually connects and persuades. That level of creative adaptation is still far beyond what AI can do.
The real value of a human translator is their ability to navigate ambiguity and context. They don't just translate what's written; they interpret what's meant. For high-stakes documents, that distinction can mean everything.
The Hybrid Model: Today's Sweet Spot
For a huge number of projects, the most effective workflow is a hybrid model that marries the best of both worlds. The process is often called Machine Translation Post-Editing (MTPE). It starts with AI generating the initial draft, handling the heavy lifting quickly and cheaply. Then, a professional human editor steps in to review and polish the output.
This editor is tasked with fixing any grammatical or terminological errors, smoothing out the flow, and ensuring the tone and cultural nuances are perfect. The hybrid approach gives you an incredible balance of speed, cost, and quality, making top-tier translation more accessible than ever. It's a game-changer in a global industry worth $72 billion, where machine translation is expected to grow by 7.1% to reach $230 million by 2026 in Europe alone. Arabic's complexity, with its intricate root system and dialects, makes it a prime candidate for this method.
This balanced workflow is perfect for larger projects like eBooks or dense technical manuals. For anyone managing these kinds of jobs, it's worth learning how AI simplifies translation workflows by tackling volume without sacrificing quality. Ultimately, it allows you to get a high-quality document translation from arabic to english without the daunting timeline or expense of a fully manual process.
Keeping Your Layout and Formatting Intact

We've all seen it happen. You spend weeks perfecting a beautifully designed Arabic PDF or EPUB, send it for translation, and get back a jumbled mess. Text overflows, tables are broken, and the entire visual structure has collapsed. It’s more than just a minor hiccup; a poorly formatted document instantly loses its professional credibility.
The main culprit here is the jump from a right-to-left (RTL) script like Arabic to a left-to-right (LTR) one like English. This isn't just about switching the text alignment. It's about flipping the entire visual flow of the page—from how images are placed to the direction of bullet points and multi-column layouts.
The RTL-to-LTR Conversion Headache
When this fundamental shift is handled poorly by an automated tool or an unprepared translator, the results are often disastrous. Imagine a technical manual where diagrams no longer point to the right instructions, or a financial report where the tables are completely unreadable. The user experience is immediately shot.
This problem is particularly acute in design-heavy formats like PDFs and EPUBs, where the layout is a critical part of the message. Good formatting guides the reader’s eye and makes complex information digestible. It's not just about looking good; it's about function.
This demand for high-fidelity localized content is fueling a massive expansion in the translation market. In the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) countries, for example, the translation services market is expected to climb to $3.8 billion by 2032. The UAE alone makes up over 40% of that market, largely driven by e-commerce giants localizing their content for a region seeing a 25% annual growth in online sales. This economic data from recent market analyses shows just how critical these advanced translation workflows have become.
Modern Tools That Automate Formatting
Thankfully, you no longer have to fix everything by hand. Modern translation platforms have been built specifically to solve this layout nightmare. Advanced tools, especially those geared toward long-form content like eBooks, use smart algorithms to analyze a document's structure before they even touch the text. They essentially map the entire layout.
These systems are smart enough to:
- Intelligently flip layouts: They automatically mirror page elements like headers, footers, and sidebars from RTL to LTR, saving you countless hours of manual work.
- Preserve design integrity: They hold onto cascading style sheets (CSS) in EPUBs and other style tags, ensuring fonts, colors, and heading hierarchies stay perfectly consistent.
- Rebuild complex elements: Tables, charts, and lists are correctly re-rendered in the LTR format so that all the data relationships remain intact.
For anyone who regularly translates complex documents, a tool with built-in layout preservation is an absolute must. It turns a tedious, multi-hour reformatting job into an automated step. Our platform, BookTranslator.ai, was designed from the ground up to manage these structural shifts, making it perfect for converting Arabic EPUBs into flawless English versions.
Best Practices for Other Workflows
What if you're not using a fully automated, layout-aware tool? You’ll need to be more hands-on. The trick is to plan ahead and set clear guidelines before the translation begins.
Your most powerful weapon for consistency is a translation style guide. Don’t just stop at tone of voice; explicitly define how visual elements like headings, lists, and captions should look in the final English document.
Here are a few practical steps you can take:
- Create a simple formatting guide: Give your translator a cheat sheet with rules for font sizes, table structures, and image alignment.
- Use master templates: If you're working in a program like Adobe InDesign, build an LTR master template first. The translator can then pour the translated text into a pre-formatted structure.
- Simplify the source file: Before sending it off, clean up the original. Get rid of any weird text boxes or clunky formatting that could trip up translation software. A cleaner source file always leads to a better output.
By thinking about these formatting challenges upfront, you ensure your final English document is not only linguistically perfect but also visually professional and ready for your readers.
Fine-Tuning Your Translation: The Crucial Role of Post-Editing and Cultural Checks
Getting that first draft of your document translation from Arabic to English feels like a major win, but the job isn't done just yet. Think of that initial translation, especially if it came from an AI tool, as a solid foundation. Now it's time for the finishing work—the quality assurance phase that turns a good-enough translation into a great one.
This step is about so much more than catching typos. It’s a deep dive to make sure the final document not only makes sense but truly connects with an English-speaking audience. If you skip this, you’re risking content that feels clunky, has embarrassing mistakes, or even worse, completely misses the point you were trying to make.
Light vs. Full Post-Editing: What's the Right Fit?
After a machine translation tool does its thing, a human expert steps in for what we call post-editing. But not all post-editing is the same. The approach you choose really boils down to who will be reading the document and why.
Light post-editing is the quick-and-dirty option. The goal here is simple: make the text understandable and clean up any glaring errors. The editor is laser-focused on fixing:
- Obvious grammatical mistakes
- Spelling errors and typos
- Incorrect terminology
- Anything the machine added or left out
This level of review is perfect for internal communications, huge batches of text needed for research, or any situation where just getting the gist of the information is enough.
Full post-editing, on the other hand, is a whole different beast. It's an intensive, line-by-line polish designed to make the translation read as if it were originally crafted in English. This is where you move beyond basic fixes to refine the style, tone, and overall flow. It’s an absolute must for any content that’s public-facing or has high stakes.
A full post-edit doesn't just ask, "Is this translation correct?" It asks, "Does this translation connect with the reader?" This shift in focus is what separates a literal translation from a truly effective one.
If you’re working on a marketing brochure, a legal contract, or a book for publication, a full post-edit is non-negotiable. It’s what protects your professional credibility and ensures your message lands with the impact it deserves.
Navigating the Minefield of Cultural and Linguistic Nuances
Often, the trickiest part of a document translation from Arabic to English has nothing to do with grammar—it's all about culture. Arabic is a language brimming with beautiful idioms, proverbs, and cultural shorthand that simply don't have a one-to-one match in English. A word-for-word translation can quickly become confusing or just plain bizarre.
For instance, take the common Arabic phrase "على رأسي" (ala ra'si). Literally, it translates to "on my head." But what it really means is "I'd be happy to" or "at your service." An English reader would be completely thrown off by the literal version.
Here’s another classic example: "القرد في عين أمه غزال" (al-qird fi ayn ummihi ghazal). Word-for-word, this means "the monkey is a gazelle in its mother's eyes." The English equivalent has nothing to do with animals—it’s simply "beauty is in the eye of the beholder."
To ensure your translated documents achieve flawless localization and resonate culturally with the target audience, exploring modern AI dubbing software platforms for flawless localization can provide insights into comprehensive content adaptation strategies.
The Human Touch Is Non-Negotiable
This is precisely why you can't skip the human reviewer. A skilled linguist—ideally a native English speaker who also has a deep understanding of Arab culture—can see these potential landmines from a mile away. They don’t just translate words; they transcreate meaning. They find the right cultural equivalent to make sure the original intent and feeling come through loud and clear.
The demand for this kind of expertise is huge. In fact, Arabic is the third most requested language for translation, fueling a massive chunk of the $71.7 billion global language services industry, which is expected to keep growing by 5.6% each year. You can find more detailed stats about this growing market and insights on the language services industry on Nimdzi.com.
Ultimately, this final quality check is about protecting your reputation. It’s the last line of defense to ensure your message is not only understood but also respected, helping you avoid the kind of cultural blunders that can erode trust and damage your brand.
Your Top Questions About Arabic to English Document Translation, Answered
When you're looking to translate documents from Arabic to English, a handful of practical questions always pop up first. How much will it cost? How long is this going to take? Do I really need a certified translation? Getting straight answers is key to planning your project well.
Let's cut through the noise. Here are the clear, no-nonsense answers to the questions we hear most often, based on years of real-world experience.
How Much Should I Expect to Pay?
The first thing everyone wants to know is the price tag. The honest answer is: it depends. The cost of translating a document from Arabic to English isn't a one-size-fits-all number, but breaking down the pricing models can give you a solid idea of what to expect.
Most professional translation is priced in one of two ways:
- Per-Word Rate: This is the industry standard for most documents—think articles, business reports, or website content. You can expect to see rates anywhere from $0.10 to $0.25 per word. The final price depends on how technical or specialized the text is.
- Per-Page Rate: You'll typically see this model for official documents like birth certificates, academic transcripts, or legal forms where word counts are fairly standard. A "page" is usually around 250 words, and pricing often starts at about $39 per page.
The complexity of your content is the biggest factor. Translating a straightforward business email will be on the lower end of that scale. A dense legal contract or a technical engineering patent, on the other hand, requires a translator with specialized expertise, and that will naturally cost more.
What's a Realistic Turnaround Time?
After cost, the next big question is always about speed. The turnaround time really boils down to the document's length and how quickly you need it. As a rule of thumb, a skilled human translator can comfortably work through about 2,000 to 2,500 words in a single day.
To give you a clearer picture, here are some typical timelines for standard projects (not rushed):
- 1-3 pages (up to 750 words): Usually back in your hands within 1-2 business days.
- 4-10 pages (up to 2,500 words): Plan for about 3-4 business days.
- Large-scale projects (over 20,000 words): This will always need a custom timeline. It’s a bigger lift that often requires a team of translators working in sync.
Need it faster? Most services offer rush options for an extra fee, often a 50% surcharge, which can essentially slice the delivery time in half. Just be sure to clarify whether the timeline is based on business days, as weekends and holidays usually aren't included.
A Pro Tip: Always try to build a small buffer into your deadline. Unexpected issues, like a tricky passage in the original Arabic or a need for clarification, can easily add a day or two to the schedule.
Do I Actually Need a Certified Translation?
This is a critical question, and the answer depends entirely on who the translated document is for. A certified translation isn't just a regular translation; it comes with a signed statement from the translator or translation agency vouching for its accuracy and completeness. Think of it as a formal guarantee.
You'll almost always need a certified translation when submitting documents for official use. This includes:
- Immigration: Any documents for U.S. Citizenship and Immigration Services (USCIS) require it.
- Academic Applications: When you're applying to a university or getting foreign credentials evaluated.
- Legal Matters: If the document will be used as evidence in a court of law.
- Government Agencies: For any official submission to a state or federal body.
For things like internal company memos, marketing copy, or personal letters, a standard, high-quality translation is perfectly fine. The key is to always check the requirements of the organization you're submitting to before you start the translation. It can save you a lot of time and headaches down the road.
Ready to translate your EPUB book from Arabic to English without losing your formatting? At BookTranslator.ai, we specialize in preserving the layout and style of your long-form documents with AI-powered precision. Get an accurate, professional-quality translation in minutes. Try it now at https://booktranslator.ai.