
Ever thought about taking a physical book from your shelf and turning it into a perfectly translated digital copy? That's the magic of the OCR and translate process. It starts with Optical Character Recognition (OCR) to pull the text from scanned pages, then uses machine translation to bring it into a new language. This guide goes way beyond simple apps, laying out a professional workflow for handling books and other long-form content with the precision they deserve.
Your Modern Workflow for Digital Book Translation
Turning a printed book into a polished, translated digital file is a real project. It’s not a one-click affair but a methodical process designed to keep the author's original voice intact while opening it up to a whole new audience. You're essentially building a bridge from the printed page to the digital screen, transforming static ink into dynamic, editable, and searchable data.
Success really comes down to a series of careful steps, with each one setting the stage for the next. Think of it like a production line for your book.
The Core Stages of Book Translation
The journey from a stack of paper to a finished EPUB or PDF involves a few distinct phases. This diagram gives you a bird's-eye view of the entire process, from getting the source material scanned to formatting the final file.
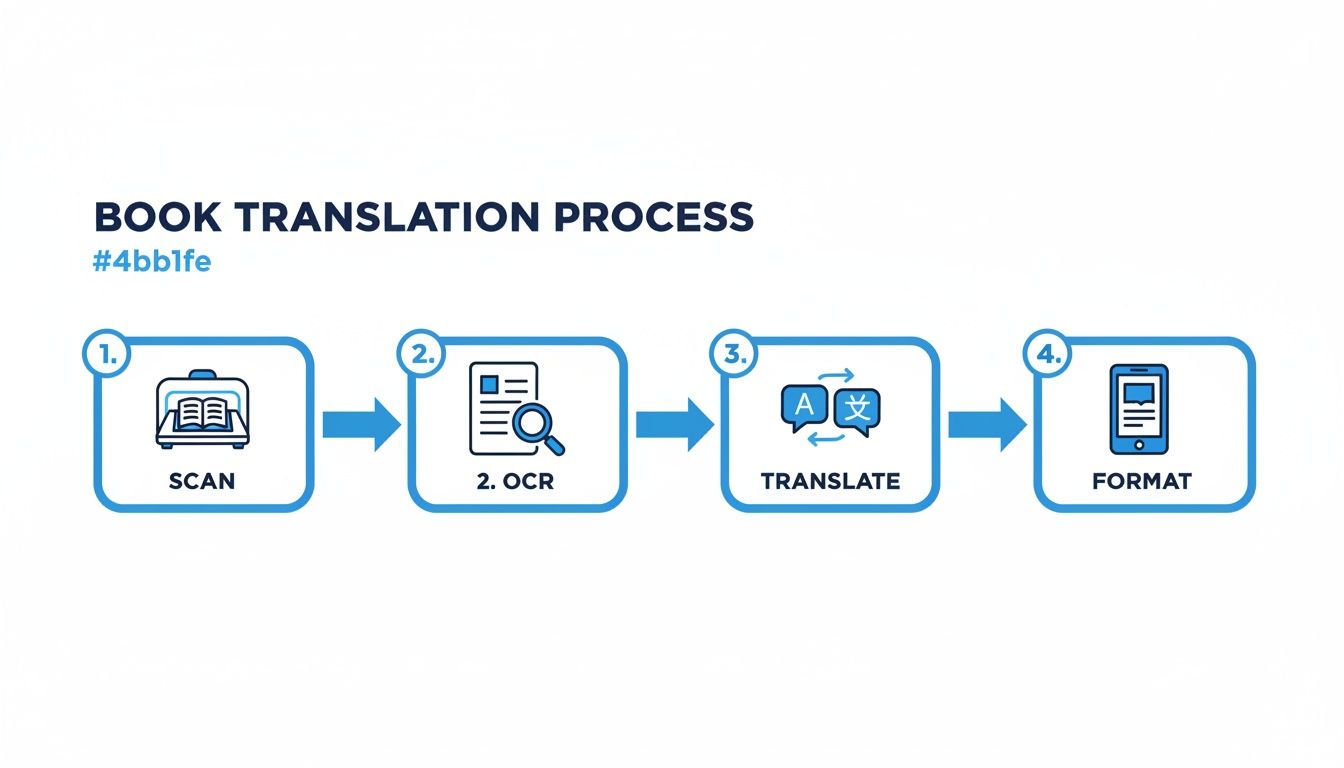
Each of these stages—Scan, OCR, Translate, and Format—is a critical link. The quality you get out of one directly determines the quality you can put into the next.
This isn't just a niche skill anymore; the demand is exploding. The global Optical Character Recognition market hit USD 13.95 billion in 2024 and is expected to soar past USD 46 billion by 2033, all thanks to the massive push for digitization worldwide.
Key Takeaway: For any large project, a structured workflow is non-negotiable. If you rush the scanning or skimp on cleaning up the extracted text, you’re just creating massive headaches for yourself down the line, especially during translation and formatting.
As part of any modern, professional workflow, it's also crucial to ensure GDPR compliant AI integration, particularly when you're handling the content of entire books. This guide will give you the complete project plan to confidently manage large-scale OCR and translation projects from start to finish.
Preparing Your Book for a Flawless Scan
Your entire OCR and translation project hinges on one thing: the quality of your initial scans. Long before you even think about running the text recognition software, you need to get this first step right. A blurry, crooked, or poorly lit scan will create a cascade of errors, leaving you with garbled text and a translation nightmare.
Think of it like cooking. The best chef in the world can't make a great meal with spoiled ingredients. Your scans are your ingredients.

This is where your scanner becomes your most important tool. Forget about using a phone app for a whole book; you'll never get the consistency you need. For a project of this scale, only a flatbed scanner gives you the control and quality required.
Dialing in Your Scanner Settings
Getting your scanner settings right isn't just a suggestion—it's absolutely critical for getting clean, accurate text. A few tweaks here can save you countless hours of painful manual corrections down the road.
I've scanned hundreds of books, from modern paperbacks to centuries-old tomes, and the right settings make all the difference. To help you get started, here’s a quick guide on what to use and why.
Optimal Scanner Settings for Book OCR
| Setting | Recommendation for Modern Books | Recommendation for Older/Complex Books | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution (DPI) | 300-400 DPI | 400-600 DPI | 300 is the minimum for clarity. Go higher for small fonts, faded ink, or complex layouts to capture more detail without ballooning file size. |
| Color Mode | Grayscale | Grayscale | Grayscale captures text nuances better than harsh black & white mode and avoids the massive file sizes and color noise of full-color scans. |
| File Format | TIFF | TIFF | TIFF is a lossless format. It preserves every single pixel perfectly, preventing the compression artifacts that JPEGs create, which can ruin OCR accuracy. |
These settings are your best bet for capturing crisp text. Remember, the goal is to give the OCR software the cleanest possible data to work with from the very start.
My Personal Rule: Never, ever use JPEG for archival scans. Its "lossy" compression literally throws away data to make files smaller, creating fuzzy artifacts around the letters. It's a shortcut that always ends up costing you more time in corrections.
Pre-Processing: The Cleanup Stage
With your pages digitized, you’re not quite ready for the OCR engine. A little bit of pre-processing will clean up the raw scans and dramatically boost your results. Most decent scanning software includes these tools, but a free image editor works just as well.
Here’s what I always check and fix:
- Deskew: This is the most important step. It automatically straightens any page that was scanned at a slight angle. Even a tiny 1-degree tilt can confuse the software, so run this on every single page.
- Crop: Get rid of the black borders and any part of the scanner lid that made it into the image. You want the software to focus only on the page content, not the junk around it.
- Contrast/Brightness: Tweak these levels to get the text as dark and the background as bright as possible. Be careful not to wash out the letters. This is a lifesaver for old books with yellowed pages or faded ink.
This careful preparation work is what separates a frustrating project from a successful one.
Once you have that pristine text extracted, you can think about the final format. If you're debating how to package your translated book, we have a helpful guide that breaks down the pros and cons of EPUB vs. PDF for AI translation.
Choosing the Right OCR Tools for Clean Text Extraction
With your pristine scans ready, it’s time to move on to the heart of the digital conversion: selecting the right Optical Character Recognition (OCR) engine. The tool you pick now directly impacts the quality of your raw text, which in turn sets the foundation for the entire translation process. When you're tackling a whole book, not just any OCR software will cut it.
You're generally looking at two paths here: powerful desktop applications or highly scalable cloud-based services. Each has its place, and the best choice really depends on the specifics of your project.

This interface from ABBYY FineReader shows off a must-have feature for serious OCR work—the ability to see the original scan and the recognized text side-by-side. It makes spotting and fixing errors a breeze.
Desktop Software vs. Cloud Services
For those who want complete, granular control over the process, a desktop application like ABBYY FineReader is a long-standing industry favorite. It's brilliant at handling complex page layouts, recognizes an enormous list of languages, and gives you tools to manually draw boxes around the exact text you want to capture. This is a lifesaver for telling the software to ignore pesky headers, footers, and page numbers.
On the flip side, you have cloud powerhouses like Google Cloud Vision OCR and Amazon Textract. These services are built for scale. Instead of tying up your own computer for hours, you can feed them hundreds or even thousands of pages at once and pay only for what you process. Their AI models are constantly being refined, so the accuracy you get right out of the box is often impressive.
My Two Cents: If I'm working on a single book with a really quirky design, I'll stick with a desktop tool for that fine-tuned control. But if the goal is to digitize a whole shelf of books with standard layouts, the sheer speed and batch-processing power of a cloud service is the only way to go.
Dialing in Your OCR Settings for Maximum Accuracy
No matter which tool you land on, don't just hit the "Go" button. Taking a few moments to configure the settings beforehand will save you from a world of manual cleanup later.
Here are the non-negotiables:
- Set the Recognition Language: This seems obvious, but it's the most crucial step. Explicitly telling the software the source language (e.g., German, Japanese, Spanish) loads the correct character sets and dictionaries, slashing the error rate.
- Define Recognition Zones: Spend a minute on a few sample pages drawing boxes around the main body of text. This is how you train the OCR to ignore the page numbers, running headers, and decorative borders that will only contaminate your final text file.
- Enable Dictionaries: If the software has this feature, switch it on. It allows the tool to check recognized words against a known vocabulary, which helps it self-correct common mistakes, like confusing "rn" for "m".
This initial setup is your first line of defense against a messy, error-filled text file.
Many of the best OCR and translation solutions are now powered by sophisticated AI; it’s worth looking into different AI tools for content creators to see what else can complement your workflow. This push for smarter technology is a huge factor in the growing translation services market, which was valued at $26.7 billion in 2024 and is on track to hit $34.24 billion by 2029. The rapid growth just shows how much demand there is for high-quality, efficient localization across the globe.
Translating Content Without Losing the Author’s Voice
Getting clean text from your OCR process is a huge step, but now comes the real challenge: translation. If you simply dump the text into a standard translation tool, you’ll get words back, but the author's soul will be gone. The result is often technically correct but emotionally flat, stripped of the very personality that made the book compelling in the first place.
The goal isn't just to swap words from one language to another. It's about faithfully transferring meaning, style, and tone. The best way to pull this off is with a hybrid approach—one that combines the raw power of AI with the irreplaceable nuance of a human expert.
Combining AI Speed with Human Insight
Modern translation platforms like DeepL have completely changed the game. They're incredibly good at understanding context and sentence structure, producing translations that feel far more natural than the clunky, literal outputs of older systems. This gives you a fantastic first draft, often knocking out in minutes what would take a human translator weeks to complete.
But for all its sophistication, AI still fumbles the subtleties. It doesn't quite get idiomatic expressions, cultural inside jokes, or the unique stylistic quirks that define an author's voice. A playful turn of phrase in Spanish, for example, can easily become stiff and overly formal in English if translated literally.
This is exactly why a final human review is absolutely essential for a high-quality result. The ideal workflow is a partnership:
- Get the AI First Draft: Start by running your clean, OCR-extracted text through a top-tier machine translation engine.
- Bring in the Human Expert: A fluent speaker then carefully reads the translated text, comparing it against the original to catch what the machine missed.
- Refine and Polish: The reviewer smooths out awkward phrasing, corrects cultural mistranslations, and fine-tunes the tone until it perfectly matches the author's intent.
This one-two punch gives you the incredible efficiency of AI without sacrificing the heart of the original work. We actually dive much deeper into this topic in our article on AI versus human translators and preserving literary style.
Using Glossaries and Style Guides for Consistency
When you're working on a project as large as a book, consistency is everything. Nothing pulls a reader out of the story faster than seeing a main character's name or a fictional city spelled differently from one chapter to the next. It just feels sloppy.
Thankfully, modern CAT (Computer-Assisted Translation) tools give you a way to enforce consistency. They let you build project-specific resources that guide the entire translation, whether it's an AI or a human doing the work.
- Translation Glossaries: Think of this as a custom dictionary for your book. You can define exactly how key terms, character names, and specific phrases must be translated every single time they appear.
- Style Guides: This is where you lay down the law on tone and formality. Should the prose be conversational or academic? Are there specific phrases you want to avoid? A style guide ensures the book reads like a cohesive whole, not a collection of disconnected chapters.
By building a simple glossary, you enforce consistency and dramatically reduce the time spent on manual corrections. It ensures that "El Bosque de las Sombras" is always translated as "The Forest of Shadows" and never "The Woods of Shade."
The engine driving all this, Machine Translation (MT), is a field that's growing incredibly fast. Valued at USD 1.12 billion in 2025, the market is projected to nearly double to USD 2 billion by 2030. This boom is fueled by Neural Machine Translation (NMT), which holds a dominant 48.67% market share thanks to its superior accuracy. As you can see from the rise of MT technology from Global Growth Insights, this technology is making sophisticated ocr and translate workflows more powerful than ever. Embracing this smart, hybrid approach is your best bet for creating a final product that truly honors the original work.
Putting It All Back Together: Crafting Your Final Digital Book
You’ve made it. The scanning, the OCR cleanup, and the careful translation are all done. Now you have a clean, translated manuscript, and it's time for the most rewarding part of the process: rebuilding it into a polished, professional digital book.
This is where all that meticulous prep work pays off. You're essentially a digital typesetter, taking the raw text and transforming it into an elegant EPUB or a crisp PDF that readers will love. This final assembly is what elevates a simple text file into a truly high-quality reading experience.
From Plain Text to a Structured Ebook
First things first, you need to bring your translated text into an ebook creation tool. For creating reflowable EPUBs—the standard for most e-readers like Kindle and Kobo—you can’t go wrong with powerful, free options like Calibre or Sigil. If your project demands a fixed layout that mimics a printed book, then Adobe InDesign is the industry-standard tool for the job.
With your text imported, the real craft begins. This isn't just a copy-paste job; you're methodically reconstructing the book's architecture to ensure it’s readable and navigable.
- Chapter Breaks: You'll need to insert clean divisions to guide the reader through the narrative.
- Headings and Subheadings: Applying proper H1, H2, and H3 tags creates a logical hierarchy and a functional table of contents.
- Text Styling: It's time to bring back the original author's intent by restoring italics, bold text, and any distinctive blockquotes.
- Image Placement: Carefully re-integrate the original illustrations, charts, or diagrams into the flow of the text.

Tools like Calibre give you an incredible amount of control, letting you fine-tune everything from the cover image and metadata to the underlying CSS that dictates the book's appearance. For a deeper dive, check out our guide on the top tools for translation-friendly formatting.
The Final QA: Validation and Polishing
Before you pop the champagne, there's one last crucial step: a thorough quality assurance (QA) check. An ebook can look flawless on your desktop but fall apart on an actual e-reader. This final pass ensures every reader gets a consistent, professional experience, no matter their device.
A word of advice from experience: Don't even think about skipping this. A single broken image or a missed chapter break can completely pull a reader out of the story and undermine all of your hard work.
Here’s what your final QA checklist should look like:
- A Full Formatting Read-Through: Go through the entire ebook with a fine-toothed comb, looking only for formatting issues. Are the headings all consistent? Do the paragraph indents look right? Are images aligned correctly and not breaking across pages?
- Test on Multiple Devices: This is non-negotiable. Load the file onto as many devices and apps as you can. A Kindle, a Kobo, Apple Books, Google Play Books—see how it looks on all of them. Reflowable EPUBs can render surprisingly differently from one platform to another.
- Run an EPUB Validation: Use an official tool like the EPUBCheck validator to make sure your file is technically sound and meets industry standards. This is your best defense against compatibility errors that can get your book rejected from online stores.
By meticulously rebuilding and polishing your digital book, you create a final product that truly honors the original work. You’ve successfully unlocked it for a brand-new audience through the ocr and translate process, and now it's ready for them to enjoy.
Common Questions About Book OCR and Translation
Even with a solid workflow, taking on a full book translation project can throw a few curveballs your way. Let's tackle some of the most common questions that pop up, from navigating legal boundaries to setting realistic expectations for your tools. Figuring this stuff out now can save you a world of hurt later.
Think of it as balancing the technical possibilities with the practical realities of the project. A little foresight goes a long way.
Is It Legal to Scan and Translate a Copyrighted Book?
This is the big one, and honestly, it lives in a legal gray area. In many places, including the United States, scanning a book you’ve purchased for your own personal use might fall under "fair use" principles. The key words there are personal use.
The moment you share, distribute, or try to sell that translated copy, you've stepped over a very clear line into copyright infringement. That’s illegal unless you have direct permission from whoever holds the copyright.
My two cents: Treat this whole process as a way to access content you already own. It's for reading books you legally bought, but in your own language. Never, ever share or sell the files you create. And always be aware of the copyright laws where you live.
How Should I Handle Complex Layouts Like Textbooks or Magazines?
Not all books are simple, straightforward blocks of text. Textbooks with call-out boxes, magazines with multiple columns, or illustrated novels can be a nightmare for basic OCR tools. This is where professional-grade desktop software really earns its keep.
A tool like ABBYY FineReader lets you manually define recognition zones. What that means is you can literally draw boxes around specific chunks of text and tell the software the exact order to read them in.
For instance, you can tell it to:
- Read the main body of text first.
- Then process the content in a sidebar.
- Completely skip page numbers, headers, and footers.
This kind of hands-on direction is crucial for preventing the OCR from mashing text from different columns together into gibberish. It takes more time upfront, for sure, but the result is a clean, logically structured text file that’s actually ready for translation.
What Kind of Accuracy Can I Realistically Expect?
You have to think about accuracy in two separate buckets: OCR accuracy and translation accuracy. They aren't the same thing.
For the OCR part, if you’re working with high-quality scans (at least 300 DPI) and a top-tier engine, you can expect over 99% character accuracy. The errors you find will be small, like mistaking an "m" for an "rn" or a "c" for an "e". A quick proofread usually catches these without much fuss.
Translation accuracy is a different beast. Modern AI translators are powerful, no doubt, but they aren't perfect. They nail grammar and direct sentence conversion, but they can easily miss the subtle stuff—cultural nuances, idioms, or the author's unique voice. A final human review is always a good idea to make sure the translation doesn't just change the words, but actually captures the spirit of the original.
Ready to bring your favorite books into your native language? BookTranslator.ai makes the process simple. Just upload your EPUB and get a professional-quality translation in minutes, with all the original formatting intact. Try it now at https://booktranslator.ai.