
How to Automate Translation Workflows with AI Tools
Want to save time and cut costs on translation projects? AI tools can automate repetitive tasks like file transfers, word counting, and assigning resources, allowing you to handle multilingual content more efficiently. By integrating AI translation platforms with project management systems, businesses have reduced turnaround times by up to 80% and costs by 30-50%.
Here’s what you’ll learn in this guide:
- How AI tools streamline translation workflows.
- Steps to set up automation, including Translation Memory and glossaries.
- Tips for maintaining quality with automated reviews and human input.
- Real-world examples of companies achieving faster, cost-effective results.
Key takeaway: Automation isn’t just about speed; it frees up your team to focus on higher-value tasks while maintaining quality. Let’s explore how to make it work for you.
Translation Workflow Automation Basics
What is Translation Workflow Automation?
Translation workflow automation streamlines the process of converting source content into translations by using an integrated system. Instead of relying on manual methods for file handling and communication, this approach automates every step - from initiating a translation request to reintegrating the translated content. At the heart of this system is a Translation Management System (TMS), which acts as a central hub. It works alongside AI-powered tools like Neural Machine Translation or Large Language Models and integrates seamlessly with content sources such as CMS platforms or code repositories[6]. When new content is added, it’s automatically queued for translation, ensuring a smooth and efficient process from start to finish.
This automation removes repetitive tasks and lays the groundwork for the impactful benefits AI tools bring to the table.
One of the standout advantages is the elimination of time-consuming manual work. When integrated with project management tools, the system handles file transfers, assigns tasks to translators based on their expertise and track record, monitors progress in real time, and conducts built-in quality checks. According to research from McKinsey, workflow automation like this could help 60% of employees save up to 30% of their time[7].
Benefits of AI Tools in Translation
AI-powered tools bring impressive efficiency to the translation process. They can cut turnaround times by as much as 80%[6] and reduce costs by 30%[7], all while improving the quality of translations. When combined with human review, these tools can boost translation accuracy by up to 30%[6]. Modern AI platforms also excel at detecting languages with over 95% accuracy and understanding context, including subtle cultural nuances.
Another major advantage is scalability. More than 60% of global companies now depend on AI to handle multilingual content demands[6]. Features like Translation Memory ensure consistency by reusing previously approved translations, while adaptive Neural Machine Translation improves over time by learning from human corrections made during the process[3]. These capabilities make AI tools indispensable for businesses managing large-scale translation needs.
This AI translation workflow replaced $300k in translation fees
How to Automate Translation Workflows Using AI Tools
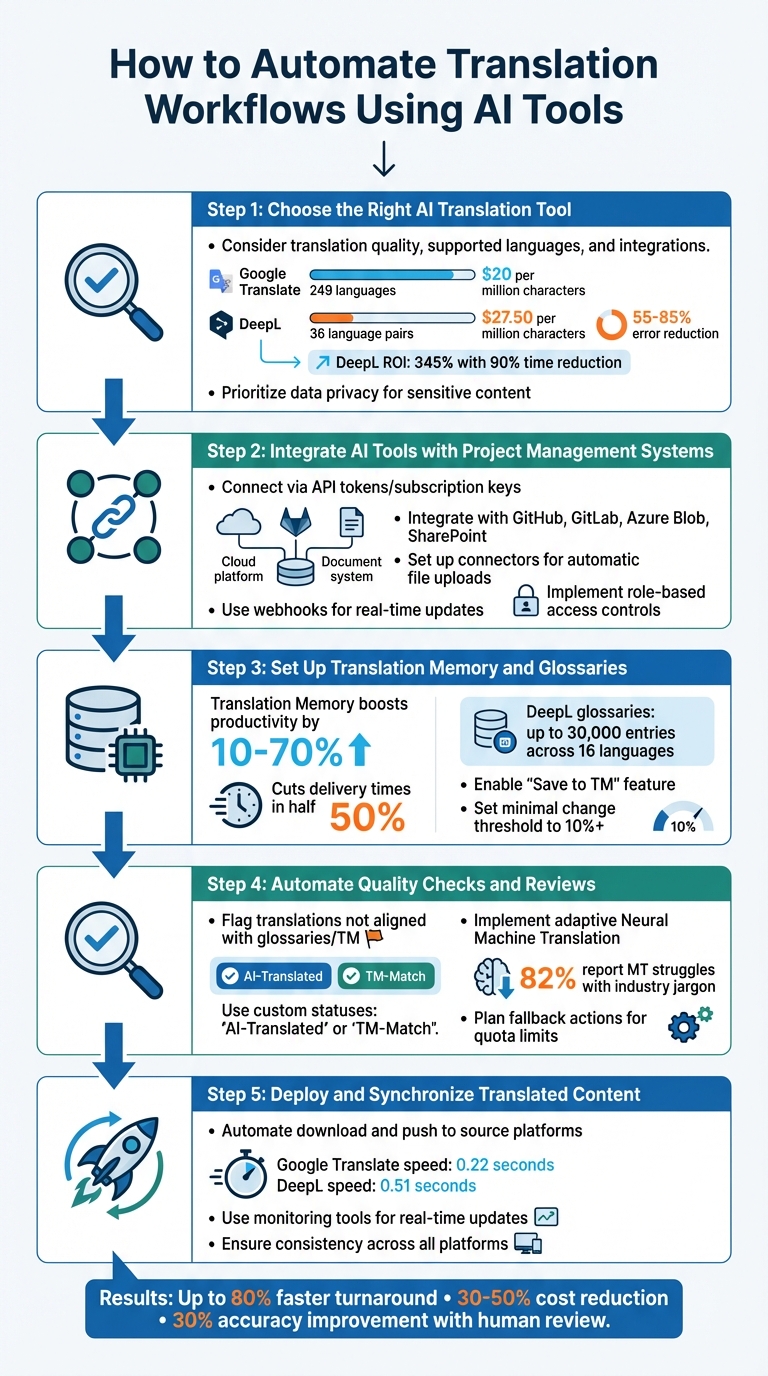
5-Step Guide to Automating Translation Workflows with AI Tools
Step 1: Choose the Right AI Translation Tool
The first step is finding a translation tool that fits your needs. Consider factors like translation quality, supported languages, and how well it integrates with your existing systems. For instance, Google Translate supports 249 languages and is ideal for handling large volumes of non-critical content. On the other hand, DeepL specializes in 36 language pairs and is known for its high accuracy, reducing errors by 55–85% across major languages. DeepL has even delivered a 345% ROI for global companies by cutting translation time by 90% and reducing workloads by 50% [8].
Match the tool to your specific content. If you're translating EPUB books, BookTranslator.ai (https://booktranslator.ai) offers one-click translation in over 99 languages. For software localization, tools like Crowdin integrate directly with code repositories, streamlining the process. Pricing is another key consideration - Google Translate costs $20 per million characters after the first 500,000 free characters each month, while DeepL Pro starts at around $27.50 per million characters [8].
If you're dealing with sensitive content, prioritize tools with strong data privacy policies. For example, DeepL Pro and ModernMT ensure your inputs aren’t used to train their models, keeping your data secure [8].
Step 2: Integrate AI Tools with Project Management Systems
Once you've selected your translation tool, connect it to your project management system to streamline the workflow. Use API tokens or subscription keys from your chosen platform to securely link it to systems like GitHub, GitLab, Azure Blob, or SharePoint [1][10].
Set up connectors to automatically upload source files to the translation tool. Configure automation rules to detect new content and trigger translation tasks instantly [1][4]. For real-time updates, use webhooks instead of manually checking the status of translations [1].
Organize your workflow with unique tags, such as ai-task-2026-01-05, to track each automated process. This makes auditing and quality control much easier. For added security in enterprise settings, use role-based access controls and managed identities to limit permissions without exposing sensitive credentials [10].
Step 3: Set Up Translation Memory and Glossaries
Translation Memory (TM) is a game-changer for efficiency. It saves previously translated text segments and reuses them for similar or identical content, boosting productivity by 10–70% and cutting delivery times in half [9]. Configure TM to prioritize 100% matches, ensuring consistent and cost-effective translations.
Glossaries are equally important for maintaining brand consistency. For example, DeepL allows business users to create glossaries with up to 30,000 entries across 16 languages [11]. Always enable the "Save to TM" feature so that AI-generated translations can be reused. Providing detailed descriptions for translation keys helps the AI interpret ambiguous phrases correctly [4].
To avoid unnecessary costs, set the "minimal change required" threshold to 10% or higher. This ensures that minor edits to the source text won’t trigger a full re-translation [4]. With TM and glossaries in place, you’re ready to focus on quality assurance.
Step 4: Automate Quality Checks and Reviews
Quality control is critical, even with automated workflows. Configure your AI to flag translations that don’t align with your glossaries or TM entries. Use custom statuses like "AI-Translated" or "TM-Match" to identify which segments need human review [4]. This ensures reviewers can focus on content that truly requires attention.
For ongoing improvement, set up adaptive Neural Machine Translation. These systems learn from human corrections in real time, refining their understanding of your brand’s tone and terminology [3]. This is especially important for technical or creative content, as 82% of survey respondents noted that standard machine translation struggles with industry-specific jargon [5].
Plan for fallback actions in your workflow. If your premium AI quota runs out, the system should switch to a standard translation tool rather than stopping altogether. For critical content like legal or marketing materials, schedule human reviews to maintain quality [4].
Step 5: Deploy and Synchronize Translated Content
Finally, automate the handover process. Set up triggers to download completed translations and push them back to source platforms [1][10]. This eliminates manual file transfers and ensures all systems stay up-to-date.
For real-time applications like website localization or customer support chats, consider the speed of your chosen tool. Google Translate processes requests in about 0.22 seconds, while DeepL averages 0.51 seconds [8]. Optimize your deployment pipeline to meet your speed requirements, and use monitoring tools to track updates to source content. This ensures translated versions remain consistent and up-to-date across all platforms.
sbb-itb-0c0385d
Best Practices for Workflow Automation
After automating your translation workflow, it's important to follow certain best practices to keep your processes secure and running smoothly.
Protect Data Privacy and Security
Data breaches can be costly - 97% of AI-related security incidents stem from inadequate access controls [12]. When automating translation workflows, safeguarding sensitive information should always be a top priority.
Avoid using public large language models for confidential content. These models often lack regulatory compliance and may expose your data. Instead, opt for AI translation tools with Zero Data Retention (ZDR) features, ensuring that your content is neither stored nor used to train public models [12]. Look for providers certified to SOC 2 Type 2 and ISO 17100, as these certifications confirm adherence to strict security and quality standards.
Set up isolated environments to separate translation data from general access. When using webhooks to connect AI tools, implement pre-shared secrets (like X-Secret headers) to verify the source of incoming requests [12]. These measures strengthen your automated workflows and protect them from potential threats. Additionally, use granular access controls to restrict access to specific parts of your translation pipeline to authorized team members only. Engage your IT, legal, and compliance teams early in the process to map out regulatory requirements, especially if your organization must comply with laws like GDPR or CCPA.
"The infrastructures that we build to support [data] aren't immutable, and aren't necessarily resilient in the face of change or catastrophe." - Jennifer King, Privacy and Data Policy Fellow, Stanford University Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI) [12]
Balance Automation with Human Review
While AI can speed up translation, it can't fully replace human judgment - especially for nuanced or critical content. Combining AI with human review enhances accuracy by up to 30% [6], and 82% of businesses report that machine translation alone struggles with industry-specific jargon [5]. The key is striking the right balance between automation and human expertise.
Adopt a hybrid workflow where AI drafts translations, and certified translators review high-stakes content like legal, medical, or marketing materials. For low-risk content, such as internal emails, you can consider bypassing human review altogether [7][15]. For example, in November 2025, Polhus implemented this approach, achieving a 75% approval rate for AI-generated translations, saving approximately $80,000 and significant time compared to traditional methods [5].
To streamline this process, configure your system to route content based on Translation Memory match percentages. For example, strings with a 95% match might skip human review, while lower matches are sent directly to editors [13]. Use AI-powered quality assurance tools to catch minor issues like capitalization, punctuation, and glossary inconsistencies before human reviewers step in. This allows linguists to focus on refining meaning and tone rather than fixing basic errors [7][5]. Don't forget to integrate human edits into your Translation Memory to help the AI improve over time [12][14].
Monitor and Improve Workflow Performance
Tracking key metrics is essential for identifying bottlenecks and refining your workflows. Focus on metrics like approval rate (the percentage of AI translations accepted without edits), turnaround time (from content submission to final deployment), and Translation Memory leverage (how often previously approved translations are reused) [6][5].
For instance, in 2025, Ajax Systems revamped their workflows with AI, producing content twice as fast and at a third of the cost compared to earlier methods [5]. They achieved these results by closely monitoring AI performance, experimenting with different configurations, and identifying the best settings for specific language pairs. Use real-time dashboards to track tasks and address delays before they impact deadlines. Analyze the history of AI prompts and responses to refine your system further.
Create a feedback loop where human corrections feed back into adaptive AI models. This ensures the system learns from past mistakes and improves over time. As your Translation Memory grows, you should see a steady drop in project costs due to increased reuse of pre-approved segments. Additionally, keep an eye on project management overhead - automation should reduce the manual hours spent on tasks like file handling and assignment [7].
"AI in localization isn't about replacing people; it's about making them more efficient." - Crowdin [5]
Conclusion
Using AI tools to automate translation workflows isn’t just about speeding things up - it’s about changing how teams handle multilingual content. By integrating AI translation platforms with project management systems, you can slash turnaround times by as much as 80% [6] and cut costs by 30% to 50% compared to traditional methods [15]. Take Polhus, for instance: they saved about $80,000, with 75% of their translations approved without any edits [5].
The real magic happens when automation and human expertise work together. AI takes care of repetitive tasks like creating initial drafts, checking for consistency, and managing files. Meanwhile, linguists can focus on the finer details, such as cultural nuances and creative touches. This collaboration can boost translation accuracy by up to 30% [6], making it easier to maintain quality across large-scale projects.
Start by pinpointing workflow bottlenecks and introducing automation step by step. Use translation memories and glossaries to keep your brand voice consistent, set up quality checks to catch errors early, and integrate AI tools directly into your content pipeline. Over time, as the system learns from human edits, you’ll notice steady gains in both quality and efficiency.
For teams diving into book translations, platforms like BookTranslator.ai make the process seamless. They offer one-click translation for EPUB files into more than 99 languages, all while keeping the original formatting and style intact. Whether you’re working on technical manuals, marketing content, or literary projects, the right AI tools can help you scale without compromising quality.
Localization is no longer static - it’s a dynamic, ever-improving process designed to help teams manage multilingual projects more effectively [2]. By applying the strategies shared in this guide, you’ll be ready to tackle increasing content demands, expand into new markets faster, and deliver reliable, high-quality translations across all your projects.
FAQs
How can AI tools enhance translation accuracy?
AI tools are transforming translation by leveraging advanced technologies like large language models (LLMs) and neural machine translation (NMT) systems. These systems are trained on extensive multilingual datasets, enabling them to grasp context, idiomatic expressions, and even industry-specific terms. The result? Translations that sound natural and stay true to the original meaning, rather than sticking to rigid, word-for-word conversions.
Many modern AI platforms also come equipped with features like real-time terminology suggestions and the ability to adjust tone, ensuring consistency throughout a project. Take BookTranslator.ai, for example - it can translate EPUB books into over 99 languages while preserving the original style, meaning, and formatting. By combining tools like these with project management systems, teams can streamline their workflows, automate the initial translation process, and focus human effort on refining the final product. This approach not only saves time but also ensures high-quality translations.
How can I integrate AI tools into my translation workflow?
To bring AI tools into your translation workflow, the first step is connecting the AI model to your system. This typically means registering the model - such as an AI-powered translation platform - and supplying the required API key to establish communication.
Once connected, craft a detailed translation prompt. Be sure to include the source and target languages, along with any specific style or terminology guidelines. Your workflow engine can then send content directly to the AI model and automatically retrieve the translated output. To streamline the process, set up webhooks or API callbacks. This ensures smooth integration with your content or project management systems, making it easy for translations to flow back into your platform without manual effort.
If you’re using BookTranslator.ai, their one-click EPUB translation service fits seamlessly into this setup. It’s designed to handle book translations efficiently, preserving both formatting and style throughout the process.
How can businesses protect sensitive data in AI-powered translation workflows?
To keep sensitive data safe in AI-powered translation workflows, businesses need to adopt strong security practices. Start by encrypting files both during transfer and while they're stored. Use secure, token-based API connections to manage access effectively. Role-based permissions and audit logs are essential for tracking who can access or modify files. For added security, running translation memories on private servers ensures proprietary terminology remains protected. Anonymizing or redacting personal data before processing also minimizes potential risks.
When choosing an AI translation platform, make sure it aligns with data protection regulations like GDPR or CCPA and has a clear, transparent privacy policy. Take time to review how the platform handles data - how it's processed, stored, and deleted. Look for features that let you decide on data location and retention policies. Regular security audits and the ability to delete files post-translation provide added peace of mind. By combining these technical safeguards with a thorough evaluation of vendors, businesses can streamline translations without compromising data security.