
AI Book Translation: Future of Global Literature Access
Only 2% of English-language books are translated, leaving millions of works inaccessible to non-English readers. AI-powered tools are changing this by translating books in minutes at a fraction of the cost. Platforms like Amazon's Kindle Translate and BookTranslator.ai are making global literature more accessible by offering translations in over 99 languages while preserving style and formatting.
Key Points:
- Cost Savings: AI cuts translation costs by up to 90%, with services starting at $5.99 per 100,000 words.
- Speed: Entire books can now be translated in minutes instead of months.
- Global Reach: AI enables access to books in "low-resource" languages like Tamil and Hausa, previously overlooked.
- Hybrid Approach: AI handles initial translations, while human editors refine tone and context for higher accuracy.
- Real Impact: Platforms like China Literature and Mantra have already translated millions of works, boosting readership and sales globally.
These advancements are reshaping book translation, making it faster, cheaper, and more accessible for authors, publishers, and readers worldwide.
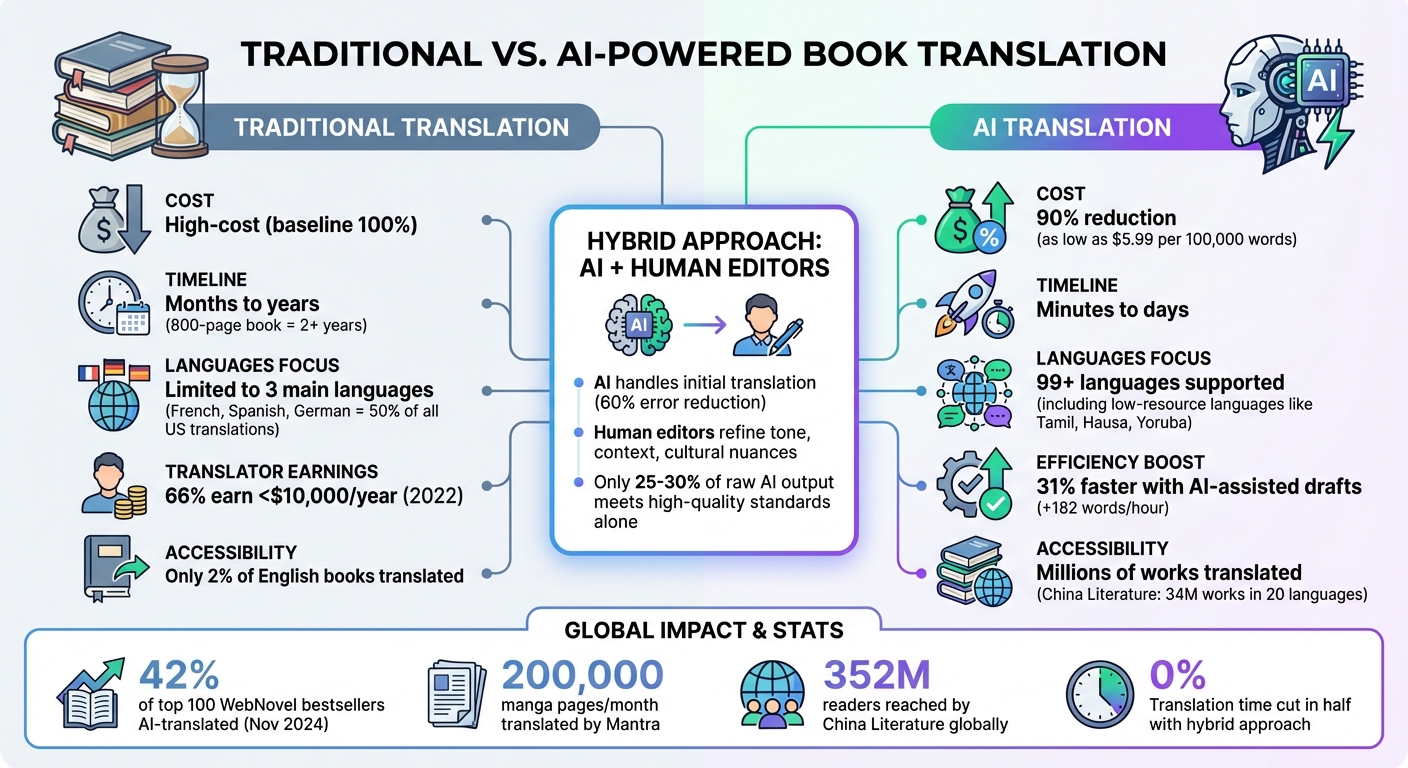
Traditional vs AI Book Translation: Cost, Speed, and Language Access Comparison
Problems with Traditional Book Translation
Expensive and Hard to Access
Cost is the biggest obstacle when it comes to traditional book translation. The process demands a mix of technical expertise and deep cultural understanding, making it both time-consuming and costly. Ilan Stavans, publisher and cofounder of Restless Books, explains:
To translate it [an 800‐page book], "substantial investment" would be necessary: Not only are "first‐rate translators" for the source language scarce, but the project would also require at least two years of dedicated work [8].
The shortage of skilled translators further compounds the issue. In 2022, nearly two-thirds of U.S. literary translators earned less than $10,000 from their work [7]. This low pay discourages talent from entering the field, especially for books with niche appeal, which often struggle to justify the costs involved. As a result, translation projects are not only expensive but also notoriously lengthy.
Slow Translation Timelines
Producing a high-quality translation isn’t just about converting words from one language to another. It involves preserving the tone, context, and unique voice of the author - a meticulous process that often takes months, if not years [8]. By the time the translation is complete, the initial excitement surrounding the book may have faded, making it harder to generate interest in the translated version. This lag in production creates a significant barrier, particularly in markets where timely access to literature is already limited.
Limited Access in Developing Regions
The challenges of cost and time hit developing regions the hardest. These areas face significant market constraints, and the limited scope of traditional translation efforts only adds to the problem. For instance, nearly half of all translated books published in the U.S. come from just three languages - French, Spanish, and German [7]. This narrow focus excludes countless works from other languages and cultures.
The PEN America Translation Committee highlights another issue:
Most publishers do not prioritize the promotion of texts in translation, thus perpetuating an underperforming cycle of comparatively low print runs and sales along with the narrow readership that follows [9].
This lack of investment creates a vicious cycle: limited promotion leads to low sales, which in turn discourages publishers from taking on more translation projects. The end result? Entire communities are left out of the global literary conversation, unable to access key works that could broaden their horizons and connect them to the world.
PETRA-E Conversations: AI and Literary Translation
How AI is Changing Book Translation
Artificial intelligence is revolutionizing book translation by using neural machine translation (NMT) and large language models (LLMs) to understand context across full sentences and documents. This approach reduces translation errors by 60% [10]. Unlike traditional methods that focus on word-for-word translation, these advanced systems analyze entire sentences to capture their meaning within the broader context. As Philippos Vassiliades puts it:
NMT marks the beginning of a new era of artificial intelligence. No longer do machines play by the rules written by linguists – instead they are making their own rules [10].
Neural Machine Translation and Large Language Models
Neural Machine Translation relies on artificial neural networks to process sentences as a whole, identifying relationships between words and phrases. Large Language Models take this a step further by using transformer architectures, which encode the relationships between words while maintaining context throughout an entire book. These models ensure a consistent tone and style by analyzing full documents. They also incorporate translation memory - storing past linguistic decisions - to improve consistency by more than 30% in larger projects [2].
The efficiency gains are hard to ignore. Human translators working with AI-assisted drafts can increase their speed by 31%, translating an additional 182 words per hour on average, with overall productivity rising by 36% [10]. By November 2024, 42% of the top 100 bestsellers on the WebNovel platform had been translated using AI [5]. These advancements not only boost accuracy but also help retain the original style of the book.
Preserving Original Formatting and Style
Accuracy isn't the only priority - maintaining the book's original formatting and style is equally crucial. AI tools ensure that layout and visual elements remain intact, simplifying the export process to publishing platforms. They can also replicate an author’s voice by adjusting parameters like formality, regional expressions, and tone to suit different genres. Some platforms even use multiple AI engines to compare outputs, selecting the version that best matches the original literary style.
For specialized texts, such as technical manuals or genre fiction with unique vocabularies, NMT systems can accurately translate 15–20% of specialized terminology when paired with domain-specific glossaries. This capability is especially valuable for works that demand precision and consistency.
Combining AI with Human Editing
While AI can handle much of the heavy lifting, human expertise is essential for refining the final product. In Post-Edited Machine Translation workflows, AI generates a draft that human editors then polish - especially since only 25–30% of raw AI output meets high-quality standards [10].
Human editors play a critical role in catching errors like hallucinations, mistranslations, or skipped content [12]. They also interpret cultural nuances and context-specific details that AI might miss. Peter Constantine, Director of the Literary Translation Program at the University of Connecticut, raises an interesting question:
What will the machine be mimicking? Is it going to do some beautiful and brilliant foreignisation, or is it going to do an amazing domestication? [10]
The combination of AI and human editing is already yielding impressive results. In April 2025, Swedish startup Nuanxed reported completing over 900 book translations using this hybrid approach. For example, the suspense novel Glen Affric by Karine Giebel was translated from French to English for HarperCollins in just a few weeks - a dramatic reduction from the months it would typically take - allowing translators to focus on creative refinement. Similarly, in June 2025, Japanese startup Mantra, supported by publishers Shueisha and Shogakukan, used AI to translate 200,000 manga pages per month into 18 languages. Human editors then reviewed the translations for accuracy, tone, and character voice, cutting overall translation time in half [11].
BookTranslator.ai: AI-Powered Book Translation Platform
With advancements in neural translation and human-AI collaboration, specialized tools are now transforming the way literature is translated. BookTranslator.ai is one such platform, designed to break down language barriers in literature. By offering affordable and efficient translation services, it enables books to cross borders with ease. The platform translates EPUB files into more than 99 languages, all while preserving the original formatting, style, and intent - solving long-standing issues in global literature distribution.
What Makes It Stand Out
At its core, BookTranslator.ai offers a seamless one-click EPUB translation feature. This tool translates entire books instantly, keeping the file structure and visual elements intact. Powered by Neural Machine Translation fine-tuned for literary works, it captures the creative tone, style, and emotional depth of the original text. Beyond translation, its smart formatting feature ensures that headings, image placements, paragraph breaks, and tables of contents remain exactly where they should be - eliminating the usual post-translation formatting struggles.
For added customization, users can upload their own glossaries to ensure consistent terminology throughout the text. Plus, the platform prioritizes security with end-to-end encryption and no data retention policies, meaning your work stays private. As Javier R., a translator who used the platform for English-to-Catalan translation, shared:
The formatting preservation is excellent! Translation quality (English to Catalan) was about 95% accurate. [13]
These features, combined with competitive pricing, make the platform accessible to writers and publishers of all sizes.
Flexible Pricing for Every Need
BookTranslator.ai uses a straightforward pay-per-book pricing model - no subscriptions required. This means you only pay for what you translate.
- Basic Plan: $5.99 per 100,000 words. Ideal for general translation needs, this plan delivers high-quality AI translations suitable for most projects.
- Pro Plan: $9.99 per 100,000 words. Designed for complex literary or technical works, this plan uses the latest premium AI models for enhanced accuracy.
Both plans have a minimum starting price of $5.99 per project and come with a money-back guarantee.
| Feature | Basic Plan | Pro Plan |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | $5.99 / 100,000 words | $9.99 / 100,000 words |
| AI Model | Standard AI | Latest Premium AI Models |
| Best For | General translation | High-accuracy literary/technical works |
| Formatting | Preserved | Preserved |
| Languages | 99+ Supported | 99+ Supported |
This pricing model can cut traditional translation costs by as much as 90% [2]. Whether you're translating widely spoken languages like English to Spanish, Chinese, or German, or tackling less common pairs like English to Swahili or Catalan, BookTranslator.ai opens up opportunities to reach audiences that were previously out of reach due to high translation costs.
sbb-itb-0c0385d
Impact on Developing Markets and Global Book Access
Lower Costs and Faster Translation
AI-driven translation is reshaping how books are shared globally by slashing costs and speeding up the process. Translation has traditionally been expensive, often making it impractical for smaller markets to access certain works. But AI has flipped the script, cutting translation costs by over 90% [6]. This dramatic reduction opens the door for niche books to be translated and distributed in emerging markets, giving readers access to works that were previously out of reach.
Take China Literature, for example - a Tencent-backed company. In December 2023, they reported that generative AI tools had boosted their translation efficiency by 100 times. This leap helped the Chinese online literature industry hit $572 million in overseas sales, marking a 40% increase compared to the previous year. It also enabled the publication of 34 million works translated into 20 languages, reaching 40 countries, including areas in Southeast Asia and Africa [6].
For scholars and researchers in developing regions, AI tools are a game changer. Non-native English speakers often face significant hurdles, spending 46.6% more time reading and 50.6% more time writing in English compared to native speakers. They’re also 2.5 times more likely to have their research papers rejected due to language issues [14]. AI-powered translation and writing tools are helping to level the playing field, reducing the time and cost of editing and making it easier for researchers in low-income regions to contribute to global academic conversations.
These advancements aren’t just theoretical - they’re already making a tangible difference.
Real Examples and Results
The practical impact of AI in translation is clear from recent initiatives. In January 2026, Mantra - a startup from the University of Tokyo supported by publishers Shueisha and Shogakukan - used AI to translate manga into 18 languages. The platform now processes 200,000 pages each month, cutting translation times in half compared to traditional methods [11]. This effort is part of a Japanese government program aimed at combating piracy by meeting global demand for translated content more efficiently.
Academic publishers are also tapping into AI’s potential. In March 2025, Taylor & Francis, a U.K.-based publisher, launched a program to translate books into English from over 30 languages using AI. Jeremy North, Managing Director of Taylor & Francis Books, explained:
Our translations program represented just the tip of the iceberg, which is why we were keen to explore whether AI could help... [it] promises to promote better understanding between cultures [16].
This initiative focuses on translating high-quality books that might not have large enough audiences to justify traditional translation costs. By using specialized glossaries, the program ensures accuracy for technical and specialized texts.
Reflecting on the broader implications, Ryan D.R. Cook, founder of Rossum Press, noted:
AI is simply the most recent in a long line of tools that make communication easier... reducing the amount of time, labour, and expense that it takes to review and translate a novel [15].
What's Next for AI Book Translation
Instant Book Translation
Imagine a world where books are instantly accessible in any language. Thanks to real-time translation powered by transformer-based AI, this vision is becoming a reality. These systems analyze entire sentences at once, making on-the-fly adjustments for accuracy and context [17][7]. And it’s not just about text anymore - AI is now capable of translating speech and video in real time. This opens up exciting possibilities, like authors hosting global book launches where their spoken words are instantly translated for audiences around the world [17].
Andy Miah, a professor at The Conversation, shares this optimistic perspective:
If AI brings us closer to a world where every book in every language is accessible to every one, then it's an extraordinary vision worth embracing. [3]
Even now, tools like MyManu’s real-time translation earbuds, initially designed for asylum seekers, hint at how this technology could reshape the literary world [3]. These advancements are setting the stage for deeper integration of translation tools within publishing platforms.
Working with Publishing Systems
AI is already making waves in the publishing industry. Platforms like Amazon’s Kindle Translate allow authors to publish fully formatted translations in just a few days [4]. Independent author Roxanne St. Claire highlights the significance of this shift:
For decades, indie authors have been unable to find a cost-effective and trustworthy solution to foreign language translation. With services like Kindle Translate, we are able to easily bring our stories to a wide international audience. [4]
Academic publishers are also embracing AI. In March 2025, Taylor & Francis announced an initiative to translate books into English for its CRC Press and Routledge imprints. This program focuses on academic works in over 30 languages, many of which previously lacked sufficient audiences to justify the high costs of human translation [16]. The approach combines AI for the initial draft with human experts refining the tone and cultural nuances. As Balint Taborski of BookTranslate describes it, this method acts as a "force-multiplier", cutting translation timelines from months to days - or even hours [18][7].
By blending real-time translation with publishing workflows, AI is not only speeding up access to literature but also laying the groundwork for a more inclusive global readership. However, these advancements also bring ethical challenges to the forefront.
Ethics and Fair Access
As AI translation becomes more widespread, ensuring equitable access across all languages and regions is a pressing concern. AI performs exceptionally well with widely spoken languages like English, Spanish, and French, but struggles with low-resource languages such as Croatian, Amharic, or Igbo, where training data is limited [1][7]. This disparity risks deepening global inequalities if not addressed.
Another challenge is what translator and professor Liesl Yamaguchi calls the "blocking effect":
A bad translation is worse than no translation because it's going to block the way to a good translation being produced. [7]
Poor-quality AI translations can mislead publishers into thinking they’ve achieved accessibility when they haven’t. Additionally, the rise of AI-driven post-editing roles is impacting professional translators' livelihoods. A 2024 survey revealed that over 33% of translators have already lost work due to generative AI tools [7]. Striking a balance between efficiency, quality, and fairness will require careful thought, especially for languages and communities that have historically been overlooked.
Conclusion
For years, nearly 98% of English-language books remained untranslated, largely due to the steep costs and time-intensive processes involved [1]. But platforms like BookTranslator.ai are changing the game, slashing translation costs by up to 90% and shrinking timelines from months to mere minutes [2][6]. This shift isn’t just about speed or savings - it’s about opening doors to voices and stories that were once sidelined, giving space to niche works and lesser-known languages.
What’s driving this change? A hybrid model that blends the precision of AI with the cultural sensitivity of human editors. AI takes care of the heavy lifting, while human experts fine-tune the cultural nuances. This balanced approach has proven effective on a large scale, with companies like Taylor & Francis and platforms such as China Literature leading the way. In fact, China Literature now connects with a staggering 352 million readers worldwide [5][6].
For independent authors and small publishers, the possibilities are even more exciting. As Senthil Nathan of Ailaysa pointed out, AI has created a global marketplace that was previously out of reach [1]. A self-published author can now share their work in languages like Tamil, Hausa, or Yoruba without spending a fortune. BookTranslator.ai makes this possible, offering translations into over 99 languages for as little as $5.99 per 100,000 words - all while maintaining the original style and formatting.
Andy Miah captures this vision perfectly:
If AI brings us closer to a world where every book in every language is accessible to every one, then it's an extraordinary vision worth embracing [3].
This vision is becoming a reality, driven by platforms that focus on affordability, accuracy, and cultural respect. With AI continuing to evolve and embed itself further into publishing workflows, the question isn’t whether global access to literature will grow - it’s how quickly it will reach every corner of the world. This progress is reshaping the literary landscape, moving us closer to true democratization of stories and ideas.
FAQs
How does AI ensure accurate and high-quality book translations?
AI leverages neural machine translation (NMT) models trained on vast multilingual datasets to produce translations that feel natural and accurate. These models don’t just swap words - they grasp the context of entire sentences, paragraphs, and even the overall narrative. This approach helps preserve the original tone, style, and subtle cultural nuances of the text.
To ensure high-quality results, AI translations often include multiple validation steps. These might involve consistency checks, specialized glossaries for important terms, and algorithms designed to treat the book as a unified whole. Many platforms also integrate human review, where editors fine-tune idiomatic phrases and refine cultural references. By blending AI precision with human expertise, these translations achieve professional publishing standards while remaining budget-friendly - sometimes costing as little as $5.99 per 100,000 words.
How do human editors contribute to AI-powered book translations?
Human editors are essential in perfecting AI-generated book translations. While AI can produce a quick and affordable initial draft, editors step in to ensure the translation reflects local nuances, maintains idiomatic expressions, and stays true to the original tone and style of the work. They refine the text by fixing errors, reworking awkward phrasing, and safeguarding the author’s unique narrative voice.
In addition to polishing the language, editors ensure consistency in formatting, punctuation, and layout - critical aspects, especially for EPUB files where design plays a significant role. Their work goes beyond just quality assurance; by providing detailed feedback, editors contribute to improving AI models over time, fostering a process of ongoing refinement while upholding high literary standards.
How is AI making literature more accessible in developing countries?
AI-powered translation is transforming how literature reaches readers in developing regions by making translations quicker, more affordable, and accessible. By automating the traditionally costly and slow process of human translation, publishers can now offer books in dozens of languages at a fraction of the usual expense. This opens the door for previously untranslated works to find new audiences.
Take platforms like BookTranslator.ai, for example. With just one click, it can translate EPUB books into over 99 languages while maintaining the original style and formatting. This breakthrough means readers in rural areas of countries such as India, Kenya, or Brazil can now enjoy global literature in their native languages. It’s breaking down language barriers and enriching the exchange of ideas across cultures.
As AI translation technology keeps advancing, it’s paving the way for a multilingual future. Stories and knowledge are no longer restricted by language, making it possible for more people to engage with global literature and expand their horizons.